Understanding the Power of SLAs
This listicle provides six practical SLA examples, from cloud availability to data recovery, relevant to teams using HubSpot and Jira. You’ll learn how clear SLAs improve performance and customer satisfaction by setting concrete expectations. We’ll also explore common SLA-related challenges and demonstrate how integrating HubSpot with Jira can alleviate these pain points, streamlining workflows and boosting efficiency for your sales, marketing, support, and product teams. This improved alignment is crucial for modern businesses relying on both platforms.
1. Cloud Service Availability SLA
A Cloud Service Availability SLA (Service Level Agreement) is a contract between a cloud provider and a customer that guarantees a certain level of uptime for the provider’s services. Think of it as a promise that your cloud-based applications and data will be accessible for a specific percentage of time. This agreement usually outlines the minimum uptime percentage (often ranging from 99.5% to a near-perfect 99.99%), how downtime is measured, and what happens if the provider fails to meet its commitment – typically through service credits or financial penalties. For businesses relying on cloud infrastructure, it’s a critical component of managing risk and ensuring operational continuity. This type of SLA is arguably the most common and vital in today’s IT landscape.

Cloud Service Availability SLAs are essential for several reasons. They provide clear financial accountability for service disruptions, helping businesses plan for potential downtime by understanding the provider’s commitments and the potential financial ramifications of outages. They also act as a differentiator between cloud providers, allowing businesses to make informed decisions based on reliability guarantees. Finally, SLAs enable accurate cost-benefit analyses by factoring in the potential cost of downtime versus the price of different service tiers. For Jira administrators, DevOps managers, and other technical roles, understanding these SLAs is paramount for building resilient systems. Sales and marketing, customer support, and even product management teams benefit from the insights derived from SLA performance, using this data to improve customer satisfaction and internal processes.
Features of Cloud Service Availability SLAs:
- Uptime Percentage Guarantees: Usually ranging from 99.5% to 99.99% per month.
- Downtime Measurement and Reporting Mechanisms: Clearly defining how downtime is tracked and reported.
- Service Credit Calculations for Outages: Specifying how credits are calculated based on downtime duration.
- Planned vs. Unplanned Maintenance Distinctions: Differentiating between scheduled maintenance and unexpected outages.
- Regional Availability Specifications: Outlining uptime guarantees for specific geographic regions.
Pros of Cloud Service Availability SLAs:
- Clear Financial Accountability: Provides recourse for service disruptions through service credits or penalties.
- Planning for Potential Downtime: Allows businesses to anticipate and mitigate the impact of outages.
- Competitive Differentiation: Helps distinguish providers based on reliability and uptime guarantees.
- Accurate Cost-Benefit Analysis: Enables informed decision-making by factoring in the cost of downtime.
Cons of Cloud Service Availability SLAs:
- Limited Recourse: Service credits often don’t fully compensate for the total business impact of an outage.
- Complex Calculations: Downtime calculation methods can be intricate and difficult to understand.
- Partial Degradation: May not account for situations where the service is partially degraded but not completely unavailable.
- Beyond Credits: Limited options beyond service credits for addressing significant or repeated SLA breaches.
Examples of Cloud Service Availability SLAs:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2: Commits to 99.99% monthly uptime.
- Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines: Guarantees 99.95% uptime.
- Google Cloud Platform Compute Engine: Offers 99.99% uptime.
- Salesforce: Provides a 99.9% system availability guarantee.
Tips for Working with Cloud Service Availability SLAs:
- Understand Downtime Calculation: Scrutinize how the provider measures and calculates downtime to avoid surprises.
- Review Exclusions: Carefully examine exclusions for planned maintenance windows, which are typically not covered by the SLA.
- Negotiate Credits: Explore the possibility of negotiating higher service credit percentages, especially for critical applications.
- Monitor Performance: Actively monitor the provider’s actual performance against their SLA commitments.
- Multi-Region Deployments: Consider deploying applications across multiple regions to mitigate the impact of single-region outages and potentially exceed single-provider SLA guarantees. This is especially relevant for teams using Jira and HubSpot, as it ensures seamless operation even if one region experiences downtime.
Cloud Service Availability SLAs are a crucial aspect of managing cloud-based services. By understanding the key features, pros, and cons, and by following the provided tips, businesses can effectively leverage these agreements to ensure the reliability and availability of their critical systems, leading to improved operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. This is especially relevant for businesses that rely on integrations like HubSpot for Jira, as a robust SLA from the cloud provider ensures that the integration remains functional and effective, contributing to smooth data flow between the two platforms. This interconnectedness highlights the importance of choosing providers with strong SLAs to maximize the benefits of integrated platforms like HubSpot and Jira.
2. IT Help Desk Response Time SLA
An IT Help Desk Response Time SLA (Service Level Agreement) is a formal contract outlining the expected timeframes for your IT support team to respond to and resolve technical issues. It’s a critical component of providing excellent customer service and ensuring smooth business operations. These SLAs utilize a tiered system, categorizing issues by severity to prioritize critical problems and allocate resources effectively. This approach ensures that urgent matters receive immediate attention while less critical requests are addressed within a reasonable timeframe. This is a prime example of an SLA, and understanding how it works is crucial for anyone managing or interacting with IT support systems. Why? Because clear expectations lead to greater satisfaction for both users and the help desk team. This structure is essential for businesses relying on efficient IT support. Learn more about IT Help Desk Response Time SLA
A successful IT Help Desk Response Time SLA implementation hinges on clear communication and well-defined processes. For example, a company might define “Priority 1” issues as those causing a complete system outage, requiring a 15-minute response and 4-hour resolution time. “Priority 2” (High) issues, such as a malfunctioning email server, might have a 1-hour response and 24-hour resolution target. By categorizing issues and setting specific targets, both the IT team and the users understand what to expect. This ultimately minimizes frustration and downtime.
Here are some actionable tips for creating and implementing an effective IT Help Desk Response Time SLA:
- Define clear criteria for each priority level: Avoid vague descriptions. Use concrete examples and measurable criteria to categorize issues.
- Establish escalation procedures: Outline clear escalation paths when deadlines are missed. This ensures timely resolution even for complex issues.
- Consider business hours: Clearly define support coverage – whether it’s 24/7 or limited to business hours. Adjust response times accordingly.
- Regularly review and adjust: Analyze performance data and adjust SLA targets based on trends and user feedback. This ensures the SLA remains relevant and effective.
- Train your staff: Ensure staff understand the ticket classification system and adhere to the established procedures. Consistent application of the SLA is key to its success.
Integrating an IT Help Desk Response Time SLA with tools like Jira Service Management or ServiceNow can significantly improve tracking and reporting. These platforms allow for automated ticket routing, escalation, and performance monitoring, making it easier to manage SLAs and identify areas for improvement.
Pros of implementing an IT Help Desk Response Time SLA:
- Clear expectations: Both users and support staff understand the expected timeframes for issue resolution.
- Improved resource allocation: Prioritization ensures efficient use of IT resources.
- Measurable performance metrics: Track and measure the team’s performance against defined targets.
- Enhanced user satisfaction: Improved response and resolution times lead to happier users and increased productivity.
Cons to consider:
- Ticket gaming: Users might inflate the severity of their issues to get faster responses.
- Complex issue dependencies: SLAs may not account for unforeseen complexities or dependencies.
- Resource intensive: Monitoring and reporting can require significant resources.
- Potential for corner-cutting: Pressure to meet targets might lead to rushed solutions and inadequate fixes.
The following decision tree illustrates the priority selection process for a typical IT help desk. This visualization helps clarify how issues are categorized and the corresponding expected response times.
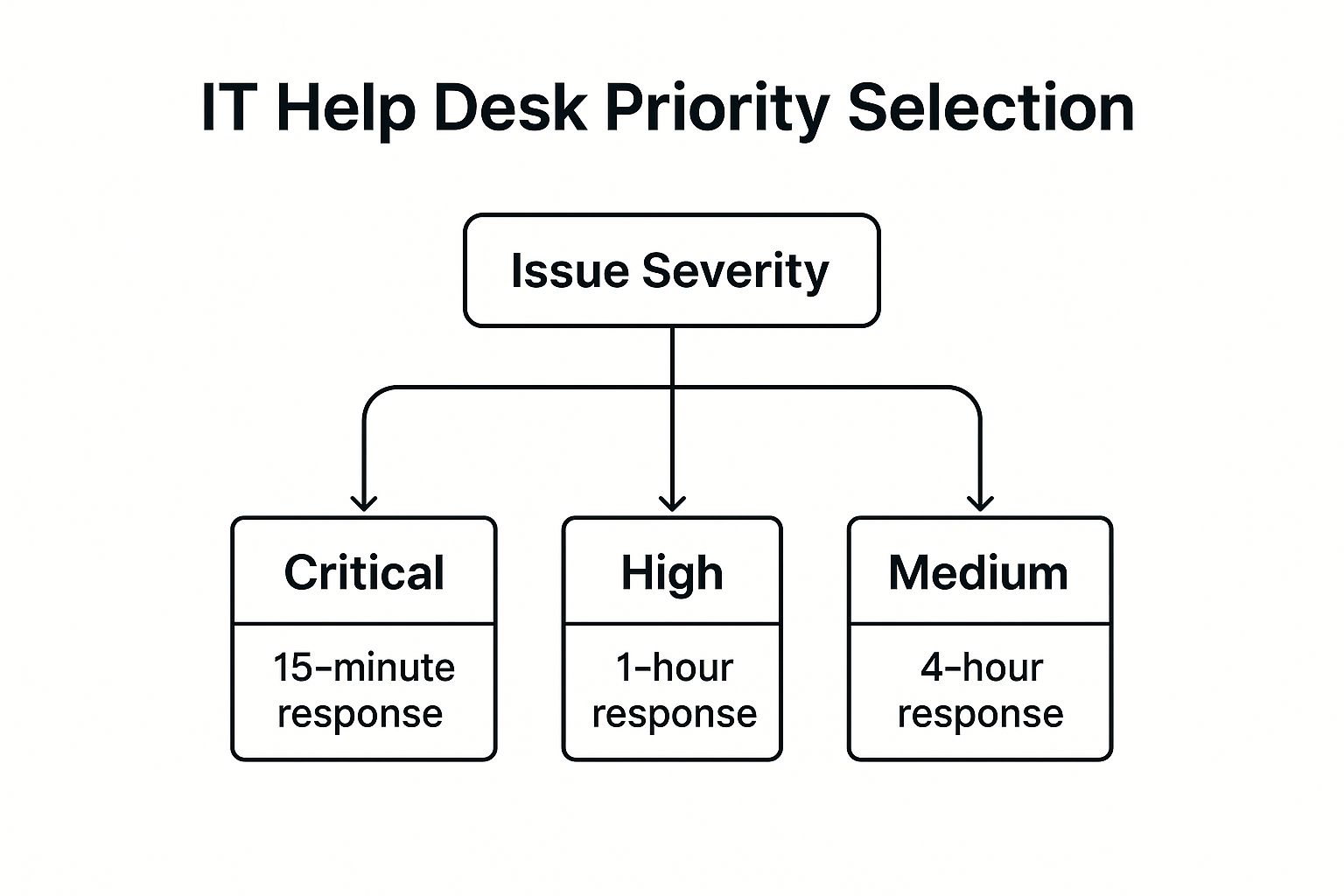
This decision tree visualizes how issue severity directly determines the initial response time. Critical issues receive the fastest response, followed by high and medium severity issues.
This example, and others like it, deserves a place on any list of SLA examples because it is a practical and common application that directly impacts user experience and business efficiency. Implementing a well-defined IT Help Desk Response Time SLA is essential for organizations seeking to streamline IT support, improve user satisfaction, and maintain smooth operations. Especially for Rev-ops leaders, support managers, and product teams using HubSpot CRM and Jira, a well-defined SLA and a seamless integration between the two platforms – such as offered by the HubSpot for Jira app – is critical for managing customer expectations and ensuring efficient issue resolution. This integration, available on the Atlassian Marketplace, facilitates two-way data synchronization, enabling teams to align their CRM and issue tracking efforts. It also allows for automatic ticket creation from HubSpot deals and enables two-way field sync, ensuring data consistency across platforms. Features like the contact/company panel and comment mirroring enhance collaboration and communication, leading to improved customer success.
3. Network Performance SLA
A Network Performance SLA (Service Level Agreement) acts as a contract between a service provider and a client, outlining specific metrics and thresholds for the quality and reliability of the network connection. It defines expectations for crucial aspects like bandwidth, latency, packet loss, and jitter, ensuring a consistent network experience. These agreements are especially vital for businesses that rely heavily on real-time applications, VoIP, video conferencing, and large-scale data transfer. A well-defined Network Performance SLA offers a quantifiable framework for measuring and managing network service quality, providing businesses with the assurance that their network infrastructure can support their operational needs. This is crucial for Jira administrators, DevOps managers, and other teams who need reliable network performance for their tools and applications.

Alt text: Diagram illustrating key components of a Network Performance SLA including bandwidth, latency, jitter, and packet loss.
Network Performance SLAs work by establishing concrete performance benchmarks. For example, an SLA might guarantee 99.99% network availability, meaning the network should be operational for all but 52.6 minutes per year. Latency thresholds, often measured in milliseconds, dictate the maximum acceptable delay for data to travel between two points. Packet loss, defined as the percentage of data packets that fail to reach their destination, is also strictly limited within the SLA. Jitter, which represents variations in latency, is especially critical for real-time applications like VoIP and video conferencing and is therefore carefully specified. By establishing these quantifiable metrics, the SLA provides a clear basis for evaluating network performance and addressing any deviations from agreed-upon standards.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Several major telecommunications providers use Network Performance SLAs to offer various levels of service. Verizon Business, for example, often guarantees 99.99% network availability and latency under 65ms. AT&T’s MPLS offerings might include SLAs with latency under 45ms and packet loss below 0.10%. Lumen Technologies (formerly Level 3) typically provides SLAs featuring 50ms round-trip latency and 99.9% availability. Comcast Business often guarantees 99.5% network uptime. These examples demonstrate how Network Performance SLAs are implemented in real-world scenarios to provide businesses with varying levels of performance assurance. These examples are relevant to anyone looking for sla examples, offering practical insights into how these agreements are structured and implemented.
Actionable Tips for Implementing Network Performance SLAs:
- Understand Measurement Points and Methodology: Ensure clarity on how and where network performance will be measured.
- Include Both Average and Worst-Case Scenarios: Don’t just focus on average performance. Consider worst-case scenarios to avoid unexpected issues.
- Specify Geographic Coverage Areas: Clearly define the geographic locations covered by the SLA, as performance can vary significantly.
- Define Remedies for Performance Degradation: Outline the actions the service provider will take in case the agreed-upon performance levels are not met. This often includes financial penalties or service credits.
- Regular Performance Monitoring and Reporting: Implement robust monitoring and reporting mechanisms to track performance against the SLA and identify potential issues proactively.
When and Why to Use a Network Performance SLA:
Network Performance SLAs are essential whenever consistent and reliable network connectivity is critical to business operations. This is particularly important for organizations relying on cloud-based applications, real-time communication tools, or large-scale data transfers. An SLA provides:
- Quantifiable network quality standards: Removes ambiguity and establishes clear performance benchmarks.
- Financial recourse for poor performance: Offers a mechanism for compensation if the service provider fails to meet the agreed-upon standards.
- Enables proper application planning: Provides the necessary information to plan and deploy applications that require specific network performance characteristics.
- Facilitates vendor comparison and selection: Offers a standardized framework for evaluating different service providers and choosing the one that best meets your needs.
Pros and Cons of Network Performance SLAs:
Pros:
- Provides clear, measurable standards for network quality.
- Offers financial recourse for substandard performance.
- Facilitates better application planning and vendor selection.
Cons:
- Can be complex to measure and monitor effectively.
- Performance can vary based on geographic location.
- May not cover all network paths used by your organization.
- Predicting the real-world impact on applications can be difficult.
For businesses heavily reliant on Jira and other integrated platforms like HubSpot, a robust Network Performance SLA is crucial. Ensuring smooth data synchronization, efficient issue tracking, and seamless communication between teams necessitates a dependable network infrastructure. By setting clear expectations and performance guarantees, a Network Performance SLA safeguards your business operations and minimizes the risk of disruptions. This type of SLA is a critical component of effective operations for Jira administrators and DevOps managers, as well as sales, marketing, customer support, product management, and data analysis teams using platforms like HubSpot. Learn more about Network Performance SLA and how it relates to capacity planning in Jira. This link can be helpful for those seeking to optimize their Jira instances for peak performance.
4. E-commerce Transaction Processing SLA
E-commerce transaction processing SLAs are crucial agreements that guarantee the performance and availability of online payment systems, shopping carts, and the entire order processing workflow. These SLAs directly impact an online retailer’s revenue generation and customer experience, ensuring smooth and reliable transactions from “add to cart” to final purchase confirmation. For businesses operating within the fast-paced world of online commerce, a robust transaction processing SLA is not just a best practice, it’s a necessity. It’s about ensuring customers can buy what they want, when they want, without any technical hiccups. For teams utilizing both HubSpot and Jira, a well-defined e-commerce transaction processing SLA becomes even more vital, ensuring that all customer-facing and backend processes are seamlessly integrated and operating at peak efficiency.

Alt text: Diagram illustrating the flow of an e-commerce transaction and the various systems involved, highlighting the importance of SLAs.
These SLAs cover key performance indicators (KPIs) such as transaction processing speed, payment gateway availability, and the system’s ability to handle peak traffic loads. They also address critical aspects like data security and compliance, setting acceptable error rate thresholds for failed transactions. For instance, an SLA might stipulate that the payment gateway must be available 99.99% of the time, or that the average transaction processing time should be under 500 milliseconds. This level of specificity provides clear expectations for both the retailer and the service provider, ensuring a consistently smooth and reliable purchasing experience for the customer. This example represents one of many sla examples that demonstrate its practical application in real-world scenarios.
Examples of successful implementation can be seen with industry leaders like PayPal, Stripe, Shopify, and Amazon Pay. PayPal boasts 99.9% payment processing availability, while Stripe guarantees API response times of under 500ms. Shopify commits to 99.98% platform uptime, and Amazon Pay maintains 99.9% service availability. These high availability and performance targets underscore the importance of robust e-commerce transaction processing SLAs in maintaining customer trust and driving revenue. These sla examples highlight how prioritizing seamless transaction processing is a key differentiator in the competitive e-commerce landscape.
Benefits of a well-defined E-commerce Transaction Processing SLA:
- Direct protection of revenue-generating activities: By guaranteeing optimal performance of critical transaction systems, these SLAs directly safeguard revenue streams.
- Clear performance expectations during peak periods: This is particularly important during high-traffic periods like sales events and holidays. This is another relevant sla example in action.
- Enhanced customer confidence and experience: Smooth, reliable transactions build trust and encourage repeat business.
- Measurable business impact metrics: The KPIs defined within the SLA provide quantifiable data to track performance and identify areas for improvement.
However, implementing and managing these SLAs is not without its challenges:
- Complex dependencies on multiple third-party services: Pinpointing the source of performance issues can be difficult when multiple vendors are involved.
- Difficulty isolating performance issues: The interconnected nature of e-commerce systems can make it challenging to identify the root cause of problems.
- High financial stakes for both parties: Downtime or performance issues can have significant financial repercussions for both the retailer and the service provider.
- Seasonal traffic variations complicate planning: Predicting and accommodating fluctuating traffic patterns can be a complex undertaking.
Actionable tips for implementing robust E-commerce Transaction Processing SLAs:
- Include peak season performance guarantees: Ensure your SLA addresses expected performance levels during high-traffic periods. This is a crucial element for effective sla examples.
- Define clear transaction volume thresholds: Establish clear expectations for handling varying transaction volumes.
- Specify performance during promotional events: Outline specific performance requirements during marketing campaigns and sales.
- Include security incident response procedures: Define a clear process for handling security breaches and data compromises. This should be a core component of your sla examples.
- Regular load testing and performance validation: Continuously monitor and test your systems to ensure they meet the defined SLA parameters.
E-commerce transaction processing SLAs are indispensable for online retailers. By establishing clear performance expectations and holding service providers accountable, these agreements protect revenue, enhance customer experience, and contribute to the overall success of an online business. For those using HubSpot for Jira, integrating SLA data into their workflows can further streamline operations and improve customer satisfaction. Leveraging the HubSpot Jira integration allows for seamless tracking of SLA performance against customer interactions, providing a holistic view of the customer journey and enabling proactive issue resolution. This exemplifies another valuable sla example, demonstrating the practical benefits of integrating different platforms. This meticulous approach to managing sla examples ensures businesses can maintain optimal performance, uphold customer satisfaction, and ultimately, drive revenue growth.
5. Software Application Performance SLA
A Software Application Performance SLA (SLA) is a contract that defines the expected performance levels of a software application. It outlines specific metrics and targets that the software vendor or internal IT team must meet. This type of SLA is crucial for ensuring that business applications meet the needs of end-users and contribute to overall productivity and efficiency. For teams utilizing integrated platforms like HubSpot and Jira, a well-defined application performance SLA ensures seamless operation and optimal data synchronization, which is vital for various business functions like sales, marketing, and customer support. This is especially important in RevOps strategies where aligning sales, marketing, and service processes is key.
Software Application Performance SLAs typically focus on areas like application response times, throughput (the amount of data processed in a given time), and system availability. For instance, a common metric might be that a specific software application must be available 99.9% of the time. Other metrics could specify the maximum acceptable response time for a user action or the number of concurrent users the system can support without performance degradation. These SLAs provide a clear understanding of what performance levels users can expect, making it easier to manage expectations and address any performance issues.
Features commonly covered by a Software Application Performance SLA include:
- Application Response Time Guarantees: Defining the maximum acceptable time for the application to respond to user requests.
- Concurrent User Capacity Specifications: Setting the number of users who can access the application simultaneously without affecting performance.
- System Availability Percentages: Ensuring the application is accessible and operational for a defined percentage of time.
- Database Query Performance Standards: Establishing acceptable response times for database queries, which are essential for data retrieval and reporting.
- User Interface Loading Time Commitments: Setting limits on the time it takes for application screens and components to load.
Pros of using a Software Application Performance SLA:
- Clear Performance Expectations for End Users: SLAs set clear expectations for users, leading to greater satisfaction and understanding of the application’s capabilities.
- Improved User Productivity and Satisfaction: When applications perform as expected, users can work more efficiently and experience fewer frustrations.
- Vendor Accountability for Application Quality: SLAs hold vendors or internal teams accountable for maintaining agreed-upon performance levels.
- Basis for Capacity Planning and Scaling: Performance SLAs provide data that can be used to plan for future growth and scale application resources accordingly.
Cons of using a Software Application Performance SLA:
- Performance Can Vary by User Location and Device: Network conditions and device capabilities can impact performance, making it challenging to maintain consistent levels for all users.
- Complex Interaction with Underlying Infrastructure: Application performance is often intertwined with the performance of the underlying infrastructure (servers, networks, databases). Isolating application-specific issues can be difficult.
- Difficult to Measure User Experience Consistently: Quantifying user experience can be subjective and difficult to measure consistently.
- May Not Account for Customization Impacts: Customizations to an application can introduce unforeseen performance issues that a standard SLA may not address.
When defining SLAs for software applications, it’s crucial to consider factors that directly impact performance and user experience. Monitoring and measuring these factors are essential for maintaining service levels. Understanding and tracking key code quality metrics can help ensure that your application remains reliable, efficient, and meets user expectations. This is especially crucial for applications like the HubSpot integration for Jira, where seamless data flow is critical.
Examples of Software Application Performance SLAs in practice:
- SAP: <2 second response time for standard transactions
- Oracle Applications: 99.5% application availability
- Microsoft Dynamics: <3 second page load times
- Workday: 99.9% system availability
Tips for creating effective Software Application Performance SLAs:
- Define Performance From the End-User Perspective: Focus on metrics that reflect the actual user experience, such as page load times and transaction completion rates.
- Include Both Peak and Off-Peak Performance Targets: Consider different performance expectations for periods of high and low usage.
- Specify Measurement Locations and Conditions: Clearly define where and how performance will be measured to ensure consistent and reliable data.
- Account for Application Customizations: If the application is customized, incorporate the potential impact of those customizations on performance.
- Regular Performance Testing and Optimization: Continuously test and optimize the application to maintain performance levels and identify potential issues proactively.
When and Why to use a Software Application Performance SLA:
A Software Application Performance SLA is particularly relevant when:
- Mission-critical applications are in use: Ensuring the availability and performance of essential applications is crucial for business continuity.
- Outsourcing application development or maintenance: SLAs provide a clear framework for managing vendor performance and ensuring accountability.
- Integrating multiple software systems: When applications interact, performance SLAs help ensure seamless data flow and interoperability. This is particularly pertinent when considering a HubSpot integration with Jira to manage workflows and client information effectively.
By including Software Application Performance SLAs in your agreements, you can foster a productive and positive user experience, maximizing the value of your software investments and promoting smooth business operations. This meticulous approach to performance management benefits various teams, from sales and marketing utilizing HubSpot to development and support teams working within Jira.
6. Data Backup and Recovery SLA
A Data Backup and Recovery SLA (Service Level Agreement) is a formal contract outlining the specific commitments a service provider makes regarding data protection and recovery. It defines the frequency of backups, how quickly data can be restored (Recovery Time Objective or RTO), and how much data loss is acceptable (Recovery Point Objective or RPO). This type of SLA is crucial for business continuity and disaster recovery planning, ensuring that vital data can be restored within defined timeframes in the event of data loss, corruption, or system failure. For teams reliant on data integrity, like those using Jira for project management and HubSpot for CRM, a well-defined Data Backup and Recovery SLA is essential for mitigating risks and maintaining operational efficiency. This section explores why this specific SLA deserves a place in any list of essential SLAs, particularly for data-driven teams.
The core of a Data Backup and Recovery SLA revolves around RTO and RPO. RTO specifies the maximum acceptable downtime after an incident before the system and data are restored and functional. RPO defines the maximum acceptable amount of data loss measured from the last successful backup to the point of failure. These metrics are directly tied to the backup frequency and the recovery procedures outlined in the agreement. For instance, a 15-minute RPO requires more frequent backups and a more robust recovery infrastructure than a 24-hour RPO. This SLA also includes data integrity verification procedures to ensure that the restored data is accurate and usable. This is critical for maintaining data consistency across platforms like Jira and HubSpot.
Several successful implementations highlight the importance of a tailored Data Backup and Recovery SLA. Veeam Cloud Connect offers a 15-minute RPO and a 1-hour RTO, suitable for businesses with low tolerance for data loss and downtime. Carbonite provides daily backups with a 24-hour recovery commitment, a more cost-effective solution for organizations with less stringent requirements. AWS Backup offers user-defined RPO/RTO with service credits for missed targets, providing flexibility and accountability. Commvault emphasizes data integrity with a guaranteed 99.9% backup success rate. These diverse examples demonstrate how Data Backup and Recovery SLAs can be tailored to fit specific business needs and risk tolerances.
Learn more about Data Backup and Recovery SLA to understand data validation techniques related to backup integrity.
Here are some actionable tips for implementing an effective Data Backup and Recovery SLA:
- Align RTO/RPO with business impact analysis: Determine the potential financial and operational impact of data loss and downtime to set realistic and achievable RTO/RPO targets. Consider the impact on Jira projects and HubSpot sales pipelines.
- Include regular recovery testing requirements: Regularly test the recovery process to validate the SLA commitments and identify potential weaknesses. This testing should involve both Jira and HubSpot data restoration.
- Specify data verification and integrity checks: Define the procedures for verifying the accuracy and completeness of restored data. This is particularly important for maintaining data consistency between Jira and HubSpot.
- Define escalation procedures for failed recoveries: Establish clear communication channels and escalation paths for situations where the recovery process fails to meet the SLA targets.
- Consider geographic distribution requirements: For enhanced resilience, evaluate the need for geographically dispersed backup locations to mitigate risks associated with regional outages.
A robust Data Backup and Recovery SLA is essential for various teams. Jira administrators and DevOps managers can ensure service availability and data protection. Sales and marketing teams using HubSpot can maintain access to crucial customer data. Customer support and service agents can rely on data availability for timely issue resolution. Product and project management teams using Jira can protect project data and maintain development timelines. Data analysts and reporting specialists can ensure data integrity for accurate insights.
Pros of a Data Backup and Recovery SLA:
- Clear data protection and recovery expectations
- Reduced business risk from data loss
- Compliance with regulatory requirements
- Predictable disaster recovery capabilities
Cons of a Data Backup and Recovery SLA:
- Complex testing and verification requirements
- High costs for aggressive RTO/RPO targets
- Dependencies on multiple infrastructure components
- Potential for partial recovery scenarios
By understanding the components, benefits, and best practices of a Data Backup and Recovery SLA, organizations can effectively protect their valuable data and ensure business continuity. This is especially important in today’s interconnected world where data synchronization between platforms like Jira and HubSpot is vital for streamlined operations and informed decision-making. This SLA provides a framework for managing expectations, mitigating risks, and achieving a predictable recovery in the face of unforeseen events.
SLA Examples Side-by-Side Comparison
| SLA Type | 🔄 Implementation Complexity | 💡 Resource Requirements | ⭐ Expected Outcomes | 📊 Ideal Use Cases | ⚡ Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Service Availability SLA | Moderate to High – requires monitoring tools and calculations | High – needs uptime tracking and multi-region setups | High uptime (99.9%-99.99%) with financial accountability | Cloud providers and businesses reliant on constant availability | Financial penalties, clear downtime accountability, planning support |
| IT Help Desk Response Time SLA | Moderate – tiered priority systems and escalation paths | Moderate to High – ongoing monitoring and reporting | Timely incident response and resolution improving user satisfaction | IT support teams managing diverse issue severities | Clear user expectations, measurable metrics, enhanced resource allocation |
| Network Performance SLA | High – involves real-time network monitoring and geographic considerations | High – complex measurement tools for latency, packet loss, jitter | Reliable network quality with defined latency and availability thresholds | Enterprises dependent on consistent network performance | Quantifiable standards, financial recourse, vendor benchmarking |
| E-commerce Transaction SLA | High – integration of multiple systems and peak traffic management | High – load testing, security compliance, and 3rd-party coordination | Fast, reliable transaction processing minimizing downtime impacts | Online retailers and payment platforms with revenue-critical operations | Protects revenue, performance guarantees under peak loads, customer confidence |
| Software Application Performance SLA | Moderate – requires performance monitoring across users and environments | Moderate – application monitoring tools and user metrics | Clear response time and availability targets ensuring user productivity | Business applications with defined user expectations | End-user focus, capacity planning foundation, vendor accountability |
| Data Backup and Recovery SLA | High – involves backup processes, verification, and disaster recovery planning | High – frequent backups, testing, and multi-site infrastructure | Predictable recovery times and data integrity assurance | Businesses requiring robust data protection and compliance | Reduces data loss risk, regulatory compliance, business continuity support |
Streamlining SLAs with HubSpot for Jira
Throughout this article, we’ve explored various SLA examples, from cloud service availability to data backup and recovery, highlighting the critical role SLAs play in maintaining service quality and customer satisfaction. We’ve also seen how disjointed systems and manual processes can hinder SLA performance, leading to missed deadlines, frustrated customers, and ultimately, business impact. Mastering these SLA concepts and approaches is invaluable for any organization striving to deliver exceptional service and maintain a competitive edge. Effectively managing your SLAs translates directly to improved customer relationships, increased operational efficiency, and better predictability in achieving business goals.
The key takeaway here is the importance of integrating your CRM and issue tracking systems to streamline SLA management. Remember those pain points we discussed earlier? Imagine eliminating the manual effort of updating tickets across platforms, or having real-time visibility into SLA performance directly within your HubSpot CRM. By connecting HubSpot and Jira, you empower your teams with the tools they need to meet and exceed SLA targets consistently. This interconnectivity fosters proactive communication, reduces response times, and ensures that everyone is working from the same information.
From sales and marketing aligning on customer onboarding to support teams efficiently resolving technical issues, the impact of seamlessly integrated SLA data ripples across your entire organization. Improved collaboration between teams translates to faster resolution times, proactive issue management, and, ultimately, happier customers.
Ready to transform your SLA management and unlock the power of interconnected workflows? Try HubSpot for Jira free today from resolution Reichert Network Solutions GmbH and experience firsthand how streamlined data synchronization can elevate your SLA performance. resolution Reichert Network Solutions GmbH provides the HubSpot for Jira integration, offering a practical solution to managing the very SLA examples we’ve discussed, helping you connect your CRM and issue tracking for optimal efficiency. Visit resolution Reichert Network Solutions GmbH to learn more and start your free trial.
