Let’s think of your organization as a bustling city, full of valuable buildings packed with important assets. Enterprise access control is the sophisticated, city-wide security system that does much more than just check IDs at the main gate. It’s the master planner that decides who gets which keys, what time they can enter certain buildings, and exactly what they’re allowed to do once inside. This system protects everything, from your physical locations to your digital worlds.
Why Enterprise Access Control Is Your Digital Gatekeeper

In a world filled with constant security threats, a smart access strategy is no longer just an IT concern—it’s the bedrock of business continuity and customer trust. At its heart, enterprise access control is the framework of rules and tech that makes sure only the right people get the right level of access to company resources.
This goes way beyond a simple username and password. We’re talking about a dynamic, intelligent system that’s constantly verifying identities and enforcing security policies across your entire operation.
The goal is actually quite simple: give seamless access to the people who need it while building an impenetrable wall against everyone else. It’s all about enabling productivity without sacrificing security.
A Foundation for Modern Business
Let’s face it, modern businesses don’t have traditional walls anymore. Employees, contractors, and partners all need access to data and tools from anywhere in the world, at any time. This distributed model creates a massive number of potential entry points for attackers.
This is exactly where enterprise access control proves its worth. It gives you a single, central way to manage and watch who’s accessing what, no matter where they are or what device they’re using. This isn’t just about stopping data breaches; it’s about building an organization that is both resilient and compliant.
A well-designed system helps you:
- Protect Sensitive Data: You can safeguard your intellectual property, customer details, and financial records from both outsiders and internal threats.
- Ensure Regulatory Compliance: Meeting standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX becomes much easier when you can generate audit trails and reports on demand.
- Improve Operational Efficiency: Automate the tedious process of onboarding and offboarding users. This frees up your IT team and kills the risk of “ghost” accounts with lingering access.
A Market Driven by Necessity
The growing focus on security isn’t just talk; you can see it in the market’s explosive growth. The global enterprise access control market, already valued at USD 12.8 billion, is expected to hit USD 13.72 billion in the coming year. This trend is only accelerating, with a projected compound annual growth rate over 9%, potentially pushing the market past USD 39.24 billion by 2037.
This rapid expansion shows just how critical this investment has become for organizations of all sizes. To better understand why enterprise access control is your ultimate digital gatekeeper, you can find more information in this a guide to access control for business security.
The Building Blocks of a Modern Access Control System
Moving from abstract ideas to a real, working security system means we need to get our hands dirty with the core components of any modern enterprise access control solution. It helps to think of it like building a secure facility. You wouldn’t just slap a single lock on the front door and call it a day. Instead, you’d design a coordinated system where every piece—from the gate guard to the keycards to the area-specific clearances—works together to protect what’s inside.
At its heart, every access control system is built on two essential pillars. Each one plays a distinct but connected role, creating a smart security structure that can adapt to how your organization actually works.
Authentication: What You Know, Have, or Are
Authentication is the very first checkpoint. It’s the simple, critical process of verifying that people are who they say they are. This is your digital bouncer, the one checking IDs at the door before anyone even thinks about stepping inside. Modern systems, of course, have moved far beyond a simple password.
- Something You Know: This is the classic factor, usually a password or a PIN. It’s the most common but also the easiest to steal or guess.
- Something You Have: This involves physical items like key fobs, smart cards, or a one-time password generated on a mobile authenticator app. It requires you to have the item on you, adding a much-needed physical layer of security.
- Something You Are: This is where biometrics come in—think fingerprints, facial recognition, or even iris scans. Because it’s tied to a unique physical trait, it’s the hardest factor to fake or share.
Truly robust enterprise access control rarely relies on just one of these. Instead, it combines two or more factors into what’s known as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), building a much higher wall for any unauthorized person to climb.
Authorization: The Rulebook for Access
Once a user is successfully authenticated, authorization kicks in. If authentication asks, “Who are you?”, then authorization immediately follows up with, “Okay, but what are you allowed to do here?” This is the rulebook that spells out the specific permissions for every single person who has been verified.
For example, a scientist in a research facility might be authorized to enter their own lab and access the project files stored on that lab’s server. But that very same authorization policy would slam the door shut if they tried to access the finance department’s records or walk into the CEO’s office.
Authorization policies are the brain of your security system. They translate high-level business rules into concrete, enforceable digital permissions, making sure the principle of least privilege—only granting the absolute minimum access needed to do a job—is applied everywhere.
The infographic below shows a pretty standard hierarchy that these authorization rules are based on.
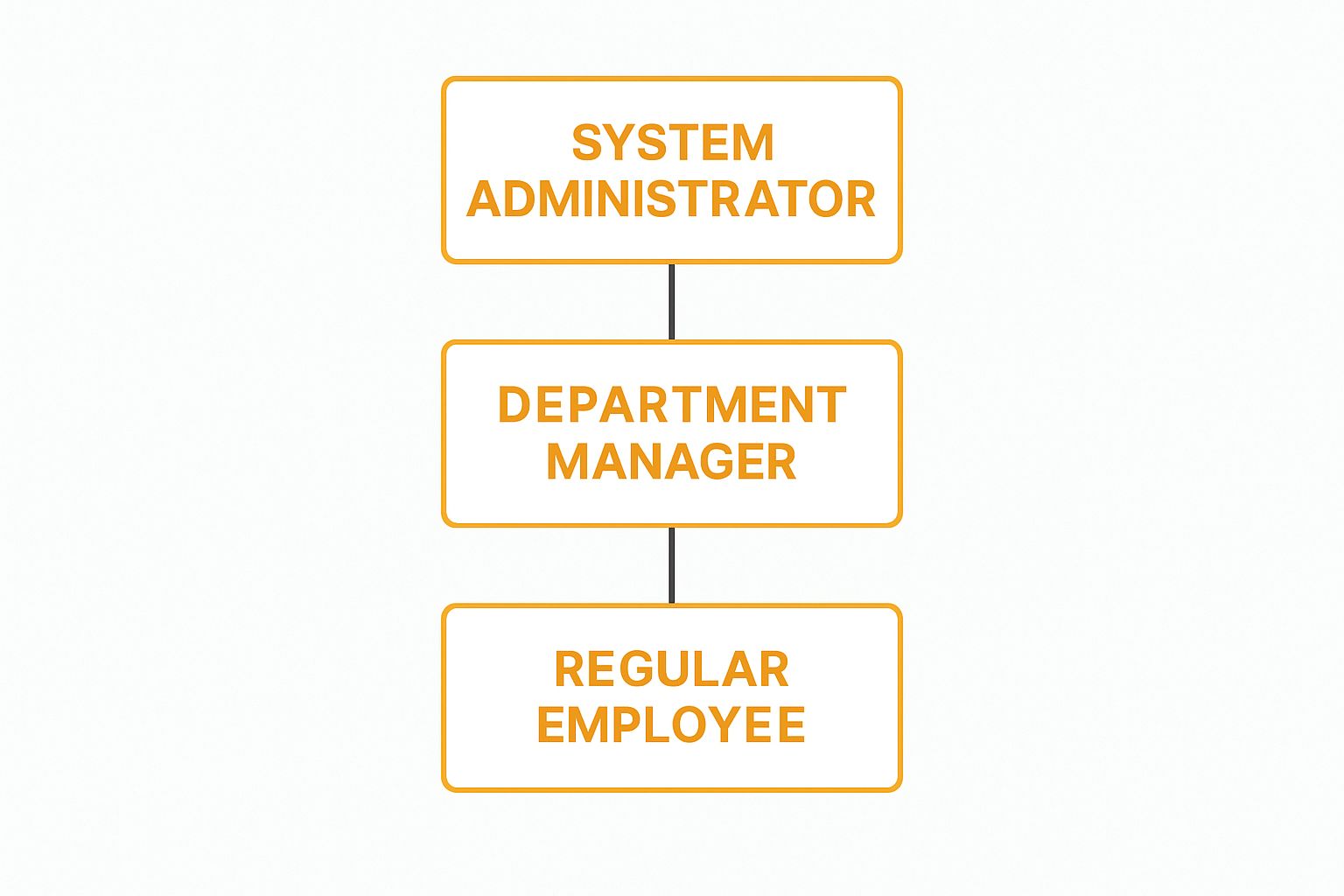
As you can see, permissions flow from the top down. System Administrators have the keys to the entire kingdom, while Regular Employees have the most restricted access, tailored specifically to their day-to-day tasks. This structure prevents both accidental mishaps and malicious actions by limiting everyone’s potential blast radius.
Choosing Your Access-Control Philosophy
Okay, you’ve got the basic building blocks in place. Now for the big question: what’s the core philosophy that will govern who gets access to what across your entire organization? This isn’t a small decision. Each model comes with its own trade-offs, and the best fit really hinges on your company’s security posture, culture, and day-to-day operational needs.
Think of these as different management styles for your digital gatekeeper. Picking the wrong one is like hiring a micromanager for a team that thrives on autonomy—it just creates friction and grinds everything to a halt.
Let’s walk through the three main models you’ll encounter: Discretionary Access Control (DAC), Mandatory Access Control (MAC), and the one you’ll see most often, Role-Based Access Control (RBAC).
Discretionary Access Control (DAC)
Imagine you give a friend a key to your house. With that key, they have the discretion to let other people in. They could even make a copy and give it to someone else without asking you first. That’s the heart of Discretionary Access Control.
In a DAC system, the owner of a resource—say, a specific Confluence page or a Jira project—gets to decide who can access it and what they’re allowed to do. It’s incredibly flexible and user-friendly, which is why you see it in environments where open collaboration and easy data sharing are the top priorities. But that flexibility is also its greatest weakness. Permissions can get messy and spiral out of control fast, making it nearly impossible to track who has access to what.
Mandatory Access Control (MAC)
Now, let’s switch gears and picture a top-secret military installation. Access isn’t handed out by individual officers. It’s dictated by a central, unchangeable system of clearance levels—think “Top Secret,” “Secret,” and “Confidential.” This is the world of Mandatory Access Control.
Under a MAC model, the system itself enforces access. It does this by comparing security labels assigned to both users (their clearance) and resources (their classification). A user with “Secret” clearance simply cannot access a “Top Secret” file. End of story. This model offers the most robust security imaginable, making it a non-negotiable for government, military, and any organization where data sensitivity is absolute. For most commercial businesses, though, its rigid nature is overkill and impractical.
The central idea behind MAC is that security policy is controlled from the top down and can’t be sidestepped by individual users. This creates a powerful defense against both insider threats and external attacks.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Finally, think about a large hospital. Access to patient records, operating theaters, and the pharmacy isn’t assigned to Dr. Smith or Nurse Jones by name. It’s tied directly to their job function: “Doctor,” “Nurse,” or “Administrator.” This is Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), and it’s by far the most popular approach for modern companies.
With RBAC, you define permissions for specific roles, then simply assign users to those roles. For instance, anyone assigned the “Accountant” role automatically gets the keys to the financial software. This approach strikes a fantastic balance between solid security and practical manageability.
One of its biggest wins is how much it simplifies the entire user lifecycle. When you’re setting up processes for user provisioning and deprovisioning, you can grant or revoke huge sets of permissions just by adding or removing a single role. It’s this scalability that makes RBAC the go-to philosophy for the vast majority of organizations today.
The Strategic Business Benefits of Access Control
It’s easy to think of enterprise access control as just a glorified lock on the door—a necessary cost for keeping the bad guys out. But that’s a massive missed opportunity. When you implement it thoughtfully, it stops being a line item on the expense sheet and transforms into a strategic asset that boosts efficiency, simplifies compliance, and even uncovers new business insights.
Think about the daily churn of people in any large company: new hires starting, contractors coming and going, employees leaving. Automating who gets access to what—and when they lose it—scraps hours of tedious manual work for your IT team. This not only gets new people productive faster but also instantly slams the door shut when someone leaves, closing one of the most common (and dangerous) security holes.
Streamlining Compliance and Reducing Risk
In today’s world, you don’t just have to be compliant; you have to prove it. For anyone who’s faced an audit for GDPR, SOX, or HIPAA, the detailed trails from a good access control system are a lifesaver. Forget the frantic, last-minute scramble to pull records together. You can generate comprehensive reports on demand.
This changes compliance from a periodic, high-stress fire drill into a quiet, automated process humming along in the background. You get concrete proof of who accessed what, from where, and when—keeping auditors happy and shielding the business from crippling fines.
For industries like healthcare, proving strict compliance with regulations like HIPAA is non-negotiable. It’s a cornerstone of any mature security program and ties directly into a broader strategy for enterprise identity management. For a deeper dive on what this looks like in practice, you can see how it applies to tools like these HIPAA compliant video conferencing platforms.
Uncovering Business Insights from Data
Here’s where it gets really interesting. The data flowing through your access control system is a goldmine of operational intelligence, if you know how to look. Analyzing traffic patterns can tell you exactly how your physical spaces are being used—or not used.
This isn’t just about security anymore. It’s about making smarter decisions on everything from real estate optimization and energy savings to workplace design. Your security tool suddenly becomes a source of business intelligence.
The market is certainly taking notice. The enterprise access control market in North America is on track to explode from USD 5.73 billion to over USD 14.19 billion in the next decade, and it’s these multifaceted benefits that are fueling the fire. This isn’t just a trend; it’s a clear signal that investing in smart access control is an investment in a safer, more efficient, and more intelligent business.
Actionable Best Practices for Implementation and Management
Putting a robust enterprise access control system in place is one thing. Actually managing it day-to-day, year after year, is a whole other ball game. Real success comes from adopting clear, repeatable practices that keep you secure without slowing down the business. Without that solid operational framework, even the most impressive tech can quickly turn into a confusing, ineffective mess.
Think of it like tending a high-security garden. You can’t just plant the seeds and walk away. It needs constant weeding, pruning, and attention to stay healthy and keep intruders out. These best practices are your essential gardening tools, helping you maintain a security posture that can flex and adapt as your organization and the threats around you change.
The heart of effective management is shifting from a reactive, “fix-it-when-it-breaks” mentality to a proactive, “always-on” security culture. Your goal should be to make strong security the path of least resistance for absolutely everyone.
Enforce the Principle of Least Privilege
If you take only one thing away from this, make it the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP). The concept is refreshingly simple but incredibly powerful: every user, device, and application should only have the bare-minimum permissions needed to do its job. Nothing more, nothing less.
An engineer has no business poking around in HR payroll data, and a marketing intern definitely shouldn’t have permissions to tweak production code. By strictly enforcing PoLP, you massively shrink your organization’s attack surface. If a user’s account ever gets compromised, the potential damage is neatly contained to their limited access, not the entire kingdom.
Applying this effectively means you need to truly understand what different roles need to function. This is where you can dig deeper into setting up granular, permission-based access control to make sure people only see and do what they’re supposed to.
Conduct Regular Access Reviews
Permissions are not a “set it and forget it” affair. People change roles, projects wrap up, and responsibilities shift. The access someone needed six months ago could be a gaping security hole today.
This is why regular access reviews are non-negotiable. At set intervals—whether that’s quarterly or semi-annually—managers and system owners must sit down and re-certify who has access to their resources. These audits are your best defense against “privilege creep,” the slow, silent accumulation of unnecessary permissions. It’s a real problem; organizations that skip this step often discover that 20% or more of their accounts are holding onto privileges they no longer need.
Automate Onboarding and Offboarding
Manually setting up and tearing down user accounts is slow, riddled with human error, and a huge security risk. The two most vulnerable moments in any user’s lifecycle are the day they start and the day they leave.
- Seamless Onboarding: Automate the process so new hires get exactly the right permissions based on their role from day one. They can be productive immediately, and IT doesn’t have to lift a finger.
- Instant Offboarding: The second an employee’s departure is official, their access to every single system must be revoked. Not in an hour, not by the end of the day—instantly and automatically. This simple step closes the door on disgruntled ex-employees causing trouble and prevents “ghost accounts” from lingering as potential backdoors.
The Future of Enterprise Access and Identity

The days of static keycards and simple passwords are numbered. The world of enterprise access control is shifting toward a future that’s predictive, seamless, and far more intelligent, all thanks to technologies that are fundamentally changing how we protect our assets. This isn’t just about building stronger locks; it’s about creating smarter, more responsive security ecosystems.
At the heart of this change are artificial intelligence and machine learning. Instead of waiting for a breach to happen, these systems analyze user behavior in real-time. They can spot anomalies and flag potential threats before they ever become a problem, turning your security from a passive guard into an active defender.
The Rise of Smarter Credentials
The physical credential itself is getting a complete makeover. Mobile access, where your smartphone acts as your badge, is quickly becoming the norm. It’s not only more convenient for users but also gives administrators a much more dynamic level of control.
At the same time, advanced biometrics like fingerprint scanning and facial recognition are moving from high-tech novelties to mainstream security tools. Paired with IoT and cloud solutions, this allows for real-time monitoring and remote management, giving organizations the flexibility they need to adapt to any situation.
This isn’t science fiction; it’s the new standard. The goal is to make security so seamless that it feels invisible to legitimate users while remaining an unbreakable barrier to threats.
Cloud Flexibility for Modern Workforces
Perhaps the biggest shift we’re seeing is the move toward cloud-based Access Control as a Service (ACaaS). As more companies adopt hybrid work models, managing access across different locations and devices has become a huge headache. ACaaS solves this by offering a single, scalable platform to oversee all your security policies from anywhere.
This cloud-first approach doesn’t just make an admin’s life easier; it guarantees your access control strategy can evolve right alongside your business. This is especially vital when managing permissions within complex environments like the Atlassian suite. For example, effective Jira access management is far simpler when it’s built on a flexible, cloud-native identity framework. These advancements are paving the way for a future where security is smarter, more adaptive, and perfectly in sync with how modern businesses actually work.
Frequently Asked Questions About Access Control
Even when you have a good handle on the core ideas, real-world questions always pop up when it’s time to actually build or manage an enterprise access control strategy. Let’s tackle some of the most common ones to bridge the gap between theory and day-to-day reality.
What Is The Difference Between Access Control and Authentication?
Think of it like getting into a secure event.
Authentication is the first step: you show your ticket and ID at the gate to prove you are who you say you are. Access control comes next, when a guard checks your ticket type—maybe it’s for VIP, maybe general admission—to decide which areas you can actually go into.
In short, authentication confirms who you are, while access control determines what you can do based on that identity.
How Does SSO Relate To Access Control?
Single Sign-On (SSO) is a really powerful tool that fits inside the larger access control framework. It works like a master key, authenticating a user just one time and then granting them access to a whole suite of approved applications. No more logging into each one separately.
SSO makes life easier for users and tightens up security by cutting down on the number of passwords that could be stolen. By centralizing authentication, it also makes it much easier for admins to manage and keep an eye on who has access to what.
This streamlined method is a cornerstone of modern security. If you want to dive deeper, our guide explains how to think of SSO as the defender of passwords.
Why Is Moving Access Control To The Cloud A Good Idea?
Shifting your access control system to the cloud brings some serious advantages, particularly for growing companies or those with a distributed workforce. The main benefits really come down to:
- Scalability: Cloud systems can grow or shrink right alongside your business needs, all without you having to buy and install new hardware.
- Remote Management: Admins can manage access rules and check on activity from anywhere in the world. This is a game-changer for supporting today’s hybrid teams.
- Reduced Overhead: You can say goodbye to maintaining on-premise servers. This lowers your operational costs and frees up your IT staff from a lot of routine maintenance.
At resolution Reichert Network Solutions, we specialize in making user management simple and cost-effective within your Atlassian environment. Our User Deactivator app automates the process of finding and disabling inactive accounts, ensuring you only pay for the licenses you actually use. Learn how to optimize your Atlassian license costs with User Deactivator.
