Stop Incidents from Derailing Your Business
Incidents disrupt operations, frustrate customers, and impact revenue. This listicle presents seven incident management best practices to minimize disruptions and build organizational resilience. Learn how to classify incidents, create effective response plans, maintain clear communication, and conduct blameless post-mortems. By implementing these incident management best practices, you’ll improve team efficiency, reduce downtime, and keep your business running smoothly. From establishing a clear framework to automating responses, these strategies empower your team to handle incidents effectively.
1. Establish Clear Incident Classification Framework
A cornerstone of effective incident management is a well-defined incident classification framework. This system categorizes incidents based on their severity, impact, and urgency, enabling organizations to prioritize response efforts, allocate resources efficiently, and trigger the appropriate response procedures. Without a clear framework, incident response can become chaotic, leading to wasted time, frustrated teams, and potentially significant business disruptions. This structured approach ensures consistency and predictability in how incidents are handled, ultimately minimizing downtime and maximizing operational efficiency. This is why it’s a crucial first step in establishing robust incident management best practices.
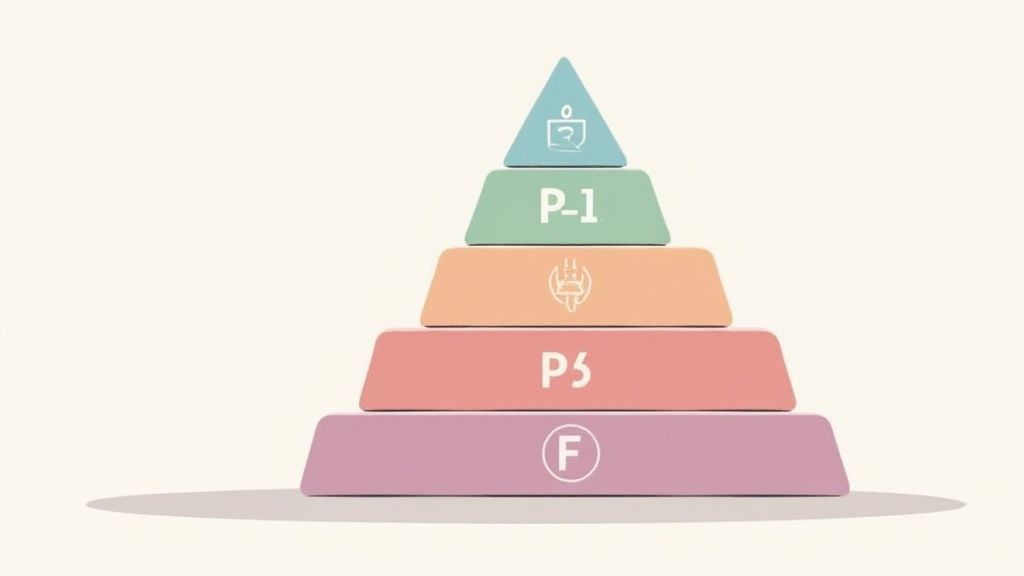
A robust incident classification framework typically includes multi-tier severity levels, often ranging from P1 (Critical) to P5 (Low) or using similar designations like Critical, High, Medium, and Low. These levels are directly tied to clear impact measurements, such as the number of users affected, potential financial impact, and the risk of reputational damage. For each severity level, documented escalation paths outline who should be notified and involved in the resolution process. Crucially, the framework also defines time-based response requirements for each severity level, ensuring that critical incidents receive immediate attention while lower-priority issues are addressed within a reasonable timeframe.
Features of an Effective Incident Classification Framework:
- Multi-tier severity levels: Typically P1-P5 or Critical, High, Medium, Low.
- Clear impact measurements: Users affected, financial impact, reputational damage, service level agreement breaches.
- Documented escalation paths: Specifies who to contact at each severity level.
- Time-based response requirements: Defines expected response and resolution times.
Pros:
- Consistency: Ensures consistent incident handling across the organization.
- Resource Optimization: Helps prevent over or under-allocation of resources.
- Clear Expectations: Provides clear expectations for response timing.
- Accurate Reporting: Facilitates accurate reporting and metrics gathering.
Cons:
- Complexity: Can become overly complex if too many classification factors are included.
- Maintenance: Requires regular updates as systems and services evolve.
- Disputes: May create friction during incidents if classification is disputed.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Google SRE: Google’s Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) team utilizes a multi-dimensional classification system considering user impact and revenue effect.
- PagerDuty: PagerDuty’s severity matrix defines P1 incidents as those affecting >20% of users with no workaround.
Tips for Implementation:
- Simplicity is Key: Limit primary severity levels to 3-5 categories for clarity.
- Objective Criteria: Use objective criteria when possible (e.g., “50% of users affected” rather than “many users”).
- Team Consensus: Build consensus on classifications across teams before implementing.
- Regular Review: Review incident classifications quarterly to ensure they remain appropriate and reflect current system architecture and business priorities.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
An incident classification framework is essential for any organization that relies on IT systems and services. It’s particularly crucial for organizations operating in regulated industries or those with complex IT infrastructures. Implementing a clear framework provides a foundation for efficient incident response, reduces the impact of disruptions, and enables continuous improvement of incident management processes. This approach is popularized by frameworks like ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library), Google’s SRE practices, and the NIST Incident Response framework, demonstrating its wide acceptance and proven effectiveness.
2. Implement Comprehensive Incident Response Plans
A cornerstone of effective incident management lies in having well-defined incident response plans. These are pre-documented procedures that act as a roadmap for teams navigating the complexities of incident resolution. They provide a structured approach, from the initial detection of an issue through to its resolution and the subsequent post-incident review. This ensures a consistent and efficient response, regardless of who is handling the incident, mitigating confusion and streamlining efforts. Incident response plans are a crucial element of incident management best practices, enabling organizations to minimize downtime and maintain service stability.
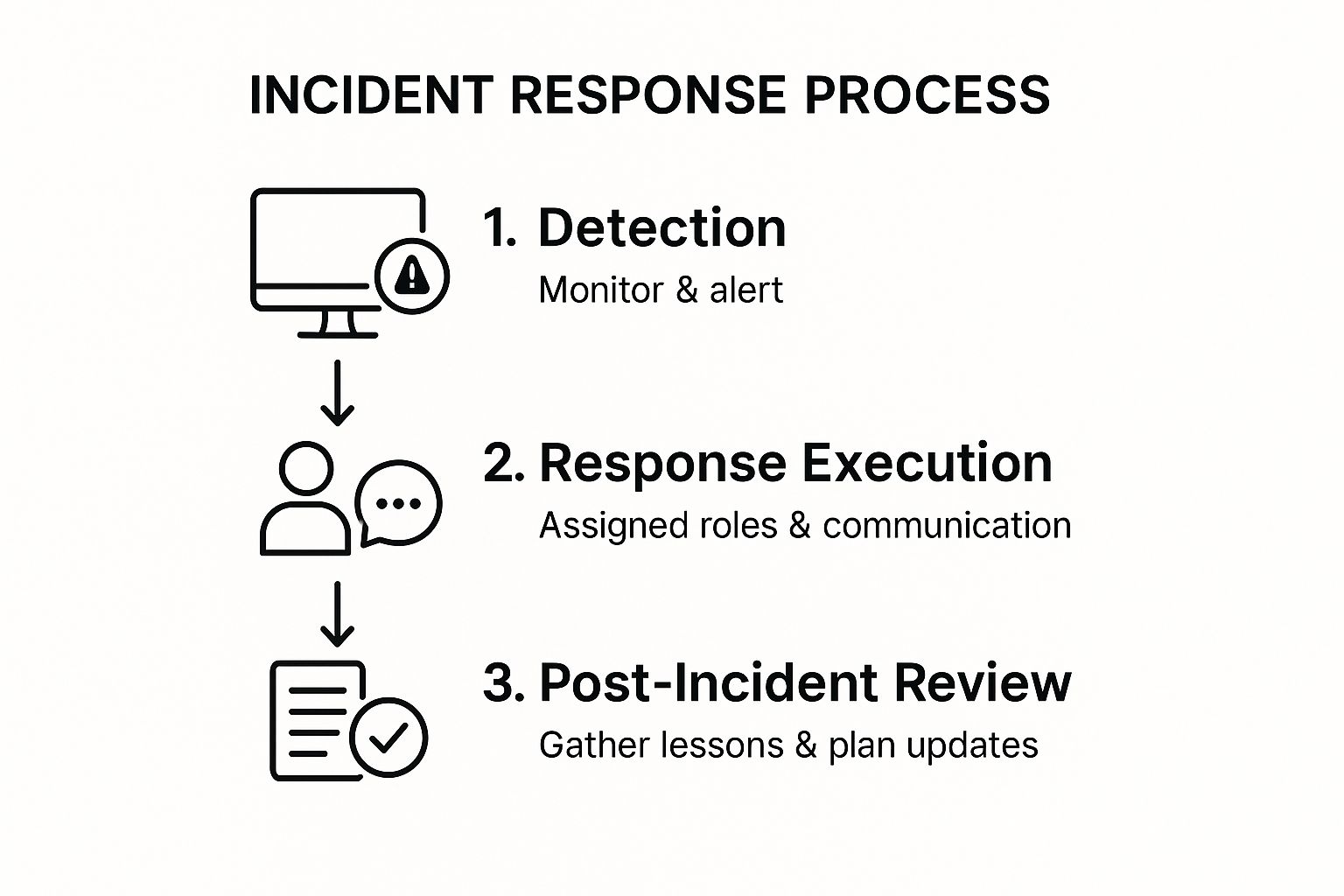
The infographic above illustrates a typical incident response process flow, starting with Incident Identification, progressing through steps like Containment, Eradication, Recovery, and culminating in Post-Incident Review. Each stage is critical, ensuring a methodical and thorough response to minimize impact and prevent recurrence. The visual representation emphasizes the importance of a structured, cyclical process for continuous improvement in incident management.
A well-crafted incident response plan details specific actions for different incident types, including clear roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, escalation paths, and documentation requirements. This structured approach provides numerous benefits: it reduces confusion during high-stress situations, accelerates mean time to resolution (MTTR), prevents critical steps from being overlooked, and facilitates knowledge transfer and cross-training.
This infographic clearly demonstrates the cyclical nature of incident management and highlights the crucial steps involved in effectively handling an incident. The flow underscores the importance of moving from reactive containment to proactive prevention through the post-incident review.
However, incident response plans aren’t without their potential drawbacks. They can become outdated if not regularly reviewed and updated, potentially creating a false sense of security if not thoroughly tested. Overly rigid plans may also stifle creative problem-solving when faced with unique or unforeseen incidents.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Slack: Maintains detailed runbooks for common failure scenarios and regularly tests these during “game days” to ensure preparedness.
- Netflix: Employs an incident response system with automated diagnosis tools that execute predefined troubleshooting steps, accelerating initial response and diagnosis.
- Microsoft Azure: Utilizes an incident management framework with specific plans for different service components, ensuring tailored responses for various scenarios.
Tips for Effective Incident Response Planning:
- Accessibility: Ensure plans are accessible in multiple formats, including offline versions, for quick reference during emergencies.
- Checklists: Include checklists for critical steps to minimize the risk of overlooking crucial tasks during incident response.
- Regular Practice: Conduct regular tabletop exercises and simulations to familiarize teams with the plans and identify areas for improvement.
- Post-Incident Reviews: Update plans after every major incident to incorporate lessons learned and refine response procedures.
- Contingency Planning: Include contingencies for situations where key personnel are unavailable, ensuring continuous coverage.
Implementing comprehensive incident response plans is essential for any organization striving for robust incident management. These plans are particularly valuable for Jira Cloud Administrators, Project Managers and Team Leads, IT Service Management Agents, Agile Software Development Teams, HR and Operations Professionals who often deal with various types of incidents. By adopting this best practice, organizations can minimize disruption, maintain service availability, and improve overall operational efficiency. You can learn more about Implement Comprehensive Incident Response Plans to further enhance your understanding. The principles of incident response planning are popularized by resources like NIST Special Publication 800-61 (Computer Security Incident Handling Guide), Amazon’s ‘Two-Pizza Teams’ approach to incident ownership, and Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) practices, providing valuable guidance for organizations seeking to improve their incident management capabilities.
3. Maintain a Single Source of Truth During Incidents
One of the most crucial incident management best practices is maintaining a single source of truth. This involves establishing a centralized, real-time record of all incident details, actions taken, and the current status. This ensures everyone involved, from technical staff to management and even external stakeholders, has access to the same accurate information. This unified view minimizes miscommunication, reduces duplicated effort, and speeds up resolution times. It also creates a comprehensive record for post-incident analysis, enabling continuous improvement of your incident management process.
This approach is particularly valuable in complex incidents involving multiple teams, shifts, or even external vendors. Imagine a scenario where your website is down. Without a single source of truth, engineers might be troubleshooting the wrong issue, customer support might be giving conflicting information, and management might be making decisions based on outdated data. A centralized platform eliminates this chaos, providing clarity and control during high-pressure situations.
Features of an effective single source of truth include a dedicated incident management tool or platform with real-time updating capabilities, a timestamped chronology of events and actions, clear ownership and status indicators, and integration with communication tools and monitoring systems. Examples of such tools include dedicated incident management platforms like PagerDuty, combined with issue tracking software like Jira, as used by Atlassian. Facebook (Meta) utilizes its internal tool “Fix It,” and Salesforce employs a centralized incident command system for multi-team responses. These real-world examples demonstrate the value and practicality of this best practice.
Pros:
- Eliminates conflicting information: Everyone works from the same dataset, preventing confusion and contradictory actions.
- Reduces time spent on status updates and coordination: No more chasing down individuals for updates; all information is readily available.
- Provides a complete audit trail for regulatory compliance: Detailed records facilitate compliance with industry regulations and internal policies.
- Facilitates seamless handoffs between teams or shifts: Incoming teams can quickly get up to speed without lengthy briefings.
Cons:
- Requires discipline to maintain during high-pressure situations: It’s easy to neglect updating the system when under stress, but consistent use is crucial.
- Potential single point of failure if the platform itself experiences issues: Redundancy and failover plans are essential.
- Can create additional administrative burden if overly complex: The system should be streamlined and easy to use, especially during incidents.
Tips for Implementation:
- Designate a specific person responsible for maintaining the incident record: This ensures accountability and consistency.
- Use templates to ensure consistent information capture: Standardized templates streamline data entry and improve searchability.
- Integrate with communication tools like Slack or Teams for automatic updates: Push notifications keep stakeholders informed without manual intervention.
- Keep entries concise and factual: Focus on objective information rather than speculation or opinions.
- Include links to relevant metrics, logs, and supporting data: This provides context and facilitates deeper analysis.
This incident management best practice, popularized by methodologies like the Incident Command System (ICS) and frameworks from PagerDuty and Atlassian, deserves its place in this list because it’s foundational to efficient and effective incident response. By centralizing information and ensuring everyone is on the same page, you empower your teams to resolve incidents faster and minimize their impact. This approach is particularly beneficial for Jira Cloud Administrators, Project Managers and Team Leads, IT Service Management Agents, Agile Software Development Teams, HR and Operations Professionals, and anyone else involved in managing incidents.
4. Conduct Thorough Blameless Post-Mortems
A critical component of effective incident management best practices is the blameless post-mortem. This structured review, conducted after an incident is resolved, focuses on identifying systemic issues and opportunities for improvement, not on assigning blame to individuals. This approach encourages honest reporting, fosters a learning culture, and ultimately leads to more effective process improvements. By shifting the focus from “who caused the problem?” to “what caused the problem?”, organizations can address the root causes of incidents and prevent them from recurring.
Blameless post-mortems are particularly valuable for Jira Cloud Administrators, Project Managers and Team Leads, IT Service Management Agents, Agile Software Development Teams, HR and Operations Professionals, and anyone involved in incident response. By understanding the systemic factors that contribute to incidents, these professionals can improve their processes, tools, and communication strategies to minimize disruptions and enhance overall efficiency.
How Blameless Post-Mortems Work:
A typical blameless post-mortem involves a structured analysis of the incident timeline and the team’s response. This analysis includes:
- Structured analysis of incident timeline and response: A detailed chronological breakdown of the incident, from the first alert to the final resolution.
- Focus on systems and processes rather than individual mistakes: The emphasis is on identifying weaknesses in the system that allowed the incident to occur, rather than blaming individuals for their actions.
- Clear identification of contributing factors: Pinpointing the specific technical, procedural, or human factors that played a role in the incident.
- Action items with owners and deadlines: Creating specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) action items to address the identified issues.
- Emphasis on preventing similar incidents in the future: The ultimate goal is to learn from the incident and implement changes to prevent similar incidents from happening again. Learn more about Conduct Thorough Blameless Post-Mortems
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Several prominent companies have embraced blameless post-mortems and demonstrated their effectiveness:
- Etsy: Known for their detailed public post-mortems, sharing their learnings and contributing to the wider tech community.
- Google: Emphasizes understanding “what happened” rather than “who caused it” in their Site Reliability Engineering practices.
- GitHub: Publishes redacted post-mortems externally, promoting transparency and sharing valuable insights.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Fosters psychological safety and encourages honest reporting.
- Identifies systemic weaknesses rather than just surface-level symptoms.
- Creates valuable organizational learning opportunities.
- Builds a knowledge base of incident patterns over time.
Cons:
- Can be time-consuming to conduct properly.
- May face cultural resistance in organizations with historically blame-oriented cultures.
- Requires diligent follow-through on action items to be truly effective.
Actionable Tips for Conducting Effective Blameless Post-Mortems:
- Use a consistent template for all post-mortems.
- Involve representatives from all affected teams.
- Focus questions on “how” rather than “who”.
- Create a public (internal) record of post-mortems that is easily searchable.
- Track action items to completion and hold owners accountable.
- Conduct the post-mortem within 48-72 hours of resolution while details are still fresh.
Maintaining a healthy and effective website also involves regular upkeep and maintenance. For example, broken links can negatively impact your SEO. Implementing effective link reclamation tactics is an important aspect of maintaining a healthy website and boosting search rankings. This can involve reaching out to websites linking to your broken pages and suggesting a replacement, or simply redirecting the broken link to a relevant, working page on your own site.
Why Blameless Post-Mortems Deserve Their Place in Incident Management Best Practices:
In today’s complex digital landscape, incidents are inevitable. However, the way organizations respond to these incidents can significantly impact their ability to learn, adapt, and improve. Blameless post-mortems provide a framework for turning incidents into valuable learning opportunities, ultimately building more resilient and reliable systems. By embracing a culture of learning and continuous improvement, organizations can minimize the impact of future incidents and build a stronger foundation for success. They are a crucial part of any robust incident management best practices strategy.
5. Implement Tiered Escalation Procedures
Effective incident management hinges on timely resolution, and a key component of achieving this is implementing tiered escalation procedures. This best practice provides a structured framework for involving additional resources or higher levels of authority when incident severity increases or the initial resolution time extends. Tiered escalation is crucial for ensuring the right expertise and decision-making power are engaged precisely when needed, preventing minor issues from escalating into major disruptions while avoiding unnecessary burdens on senior resources for routine incidents. This makes it a critical incident management best practice for any organization.
How Tiered Escalation Works:
A tiered escalation system typically involves multiple levels of support, each with increasing levels of expertise and authority. The process begins with the first point of contact, often a service desk or frontline support team. If they cannot resolve the incident within a predefined timeframe or if the incident’s complexity exceeds their capabilities, it’s escalated to the next tier. This continues until the incident is resolved. Each tier operates according to defined service level agreements (SLAs) that dictate response times and resolution targets.
Features of Effective Tiered Escalation:
- Clearly Defined Escalation Triggers: These triggers are based on objective criteria, including time elapsed, impact assessment (e.g., number of users affected, financial impact), and incident complexity.
- Multiple Tiers of Response Teams: Each tier possesses progressively higher levels of expertise and decision-making authority.
- Documented On-Call Rotations and Contact Procedures: This ensures that the right people can be reached quickly, regardless of the time or day.
- Integration with Notification Systems: Automated notifications keep stakeholders informed of the incident’s progress and any escalations.
- Defined Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Each tier’s response and resolution time is governed by SLAs, ensuring accountability and predictable response patterns.
Pros:
- Prevents minor incidents from unnecessarily consuming senior resources.
- Ensures timely involvement of the appropriate expertise, leading to faster resolution of complex issues.
- Creates predictable patterns for incident response, simplifying management and reporting.
- Provides clear accountability at each stage of the escalation process.
Cons:
- If escalation thresholds are set too conservatively, it can delay resolution.
- Bottlenecks can occur if higher tiers are understaffed.
- Requires a careful balance between empowering teams with autonomy and maintaining appropriate oversight.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS escalates to dedicated incident managers for significant service disruptions, ensuring rapid response and communication to affected customers.
- Microsoft: Their tiered support model escalates from frontline support to specialized engineering teams based on clearly defined criteria.
- IBM: IBM employs a Critical Situation Management process for incidents with significant enterprise impact, engaging senior leadership and specialized response teams.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Create clear, objective criteria for escalation: Avoid ambiguity and ensure everyone understands the triggers.
- Include both time-based and impact-based escalation triggers: This provides a comprehensive approach to escalation.
- Empower first responders to escalate based on their gut feeling: Sometimes, even if criteria aren’t formally met, an experienced responder may sense the need for escalation. Trust their judgment.
- Review escalation patterns regularly to identify optimization opportunities: Analyze historical data to refine triggers and resource allocation.
- Maintain up-to-date contact information for all escalation tiers: Ensure that communication channels are always open.
Learn more about Implement Tiered Escalation Procedures
This approach is especially beneficial for Jira Cloud Administrators, Project Managers and Team Leads, IT Service Management Agents, Agile Software Development Teams, and HR and Operations Professionals who are frequently involved in incident management processes. By adopting tiered escalation procedures, these professionals can ensure efficient and effective incident resolution, minimizing disruption and maximizing productivity. This best practice aligns well with frameworks such as the ITIL Service Management framework, ISO/IEC 27035 (Information security incident management), and the follow-the-sun support models used by global organizations.
6. Develop Effective Communication Protocols
Effective communication is the cornerstone of successful incident management. Incident communication protocols define how information about incidents is shared both internally among response teams and externally with stakeholders like executives and customers. These protocols ensure timely, accurate, and appropriate information reaches everyone who needs it, helping to coordinate response efforts, manage expectations, and maintain trust. This is crucial for minimizing disruption and returning to normal operations as quickly as possible, making it a critical incident management best practice.

Well-defined communication protocols incorporate several key features: pre-written templates for various communication types (e.g., initial alerts, status updates, resolution notifications), dedicated communication channels for different audiences (e.g., a Slack channel for technical teams, a status page for customers), clearly defined roles outlining who communicates what to whom, a regular cadence for updates during extended incidents (e.g., every 30 minutes), and guidelines for tone and content appropriate to each audience (technical details for engineers, business impact for executives).
Benefits of Effective Communication Protocols:
- Reduces speculation and rumors: Consistent updates from a trusted source minimize misinformation and anxiety during stressful incident situations.
- Prevents conflicting messages: Having designated communicators and pre-approved messaging avoids confusion caused by conflicting information from multiple sources.
- Helps maintain customer trust through transparency: Open and honest communication, even when things go wrong, builds trust and strengthens customer relationships.
- Allows technical teams to focus on resolution rather than constant updates: Designated communication leads free up technical resources to concentrate on resolving the incident.
Potential Drawbacks:
- Bureaucracy: Overly complex protocols with multiple layers of approval can slow down communication and hinder the response process.
- Slowed Communication: Long approval chains can delay critical updates from reaching stakeholders.
- Balancing Transparency and Security: Sharing information openly while protecting sensitive data requires careful consideration and planning.
Real-World Examples:
- Cloudflare: Their detailed technical post-mortems on their blog following major incidents provide transparency and valuable insights for the wider technical community.
- Slack: Their status page updates keep users informed about service disruptions, including both technical details and business impact.
- Zoom: Their COVID-era incident communications effectively balanced technical details with user-friendly explanations, addressing a broader audience with varying technical expertise.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Designate specific individuals as communication leads during incidents. This allows for centralized and consistent messaging.
- Create pre-approved templates for common incident types. This speeds up communication and ensures consistency.
- Establish a regular cadence for updates (e.g., every 30 minutes for critical incidents) to keep stakeholders informed.
- Train technical teams on how to communicate clearly to non-technical audiences. This bridges the communication gap and ensures everyone understands the situation.
- Set up dedicated channels (Slack, Teams, etc.) for incident communications to keep discussions focused and organized. Learn more about Develop Effective Communication Protocols for creating internal communication plans.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
Effective communication protocols are essential for any organization that relies on technology and services. Whether you’re a Jira Cloud administrator, a project manager, an IT service management agent, part of an agile software development team, or in HR and operations, implementing robust communication protocols is a crucial incident management best practice. They are especially vital during major incidents, but the benefits extend to everyday problem-solving and communication within and outside the organization. Frameworks like Statuspage by Atlassian, PagerDuty’s Stakeholder Communications framework, and ITIL Communication Management processes provide excellent resources for developing and refining your approach.
7. Automate Incident Detection and Response
In the fast-paced world of modern IT, rapid incident detection and response are crucial for minimizing downtime and maintaining service availability. Automating these processes is a key incident management best practice that empowers organizations to proactively address issues before they escalate into major disruptions. This approach involves using technology to detect anomalies, trigger alerts, and even execute initial response actions without human intervention. This not only reduces detection time and eliminates tedious manual monitoring tasks but also enables a faster initial response to common incident types, contributing significantly to improved service reliability and customer satisfaction.
This approach leverages intelligent monitoring systems with anomaly detection capabilities, automatically triggering alerts based on predefined thresholds. Runbook automation handles common remediation steps, while self-healing capabilities address known issues automatically. Integrating monitoring, ticketing, and communication tools ensures seamless information flow and collaboration throughout the incident lifecycle. For Jira Cloud Administrators, Project Managers, and Team Leads, this translates to less time firefighting and more time focusing on strategic initiatives. IT Service Management Agents benefit from reduced workload and faster resolution times. Agile Software Development Teams can maintain their sprint velocity by minimizing disruptions caused by incidents. Even HR and Operations Professionals can benefit from automated notifications related to systems impacting their work.
Consider these examples of successful implementation: Netflix utilizes tools like Chaos Monkey to proactively inject failures and test the resilience of its systems, coupled with automated remediation systems. Google leverages AI for predictive failure analysis and automated response, proactively preventing potential outages. Microsoft Azure offers automated health checks and self-healing capabilities, ensuring high availability of its cloud services. These examples highlight the power of automation in minimizing downtime and maintaining service reliability. You can learn more about Automate Incident Detection and Response to explore the available tools and their applications in more detail.
Features of Automated Incident Detection and Response:
- Intelligent monitoring systems with anomaly detection
- Automated alerting based on predefined thresholds
- Runbook automation for common remediation steps
- Self-healing capabilities for known issues
- Integration between monitoring, ticketing, and communication tools
Pros:
- Dramatically reduces mean time to detect (MTTD) incidents
- Eliminates human error in routine response procedures
- Enables 24/7 monitoring without staffing constraints
- Frees up human resources for complex problem-solving
Cons:
- Upfront investment in tools and integration can be significant
- Risk of alert fatigue if thresholds aren’t properly tuned
- May miss novel or complex issues that don’t match predefined patterns
- Requires ongoing maintenance as systems evolve
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Start small: Begin by automating detection before moving to automated remediation.
- Human oversight: Implement ‘human in the loop’ approvals for high-risk automated actions.
- Continuous improvement: Track false positive/negative rates to continuously improve detection accuracy.
- Progressive automation: Build automation that starts with simple cases and expands over time.
- Documentation: Document all automated responses clearly for transparency.
Automating incident detection and response is a crucial component of modern incident management best practices. While it requires initial investment and ongoing maintenance, the benefits of reduced MTTD, improved efficiency, and increased service availability make it a worthwhile investment for organizations of all sizes. By following the tips provided and learning from industry leaders, you can effectively implement automation and strengthen your incident management capabilities. This approach aligns perfectly with Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) practices, the DevOps movement, and the growing field of AIOps (Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations).
7 Key Incident Management Practices Comparison
| Best Practice | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Establish Clear Incident Classification Framework | Medium – requires consensus and updates | Moderate – documentation and training | Consistent prioritization and allocation | Organizations needing structured incident prioritization | Prevents resource misallocation; clear escalation |
| Implement Comprehensive Incident Response Plans | High – detailed plans and regular updates | High – multi-team coordination and training | Reduced confusion; faster resolutions | Teams managing diverse incident types under pressure | Improves coordination; ensures critical steps |
| Maintain a Single Source of Truth During Incidents | Medium – tool integration and discipline | Moderate – incident management platforms | Reduced miscommunication; audit-ready records | Distributed teams requiring real-time status sharing | Eliminates conflicting info; seamless handoffs |
| Conduct Thorough Blameless Post-Mortems | Medium – structured review sessions | Low to moderate – time and facilitation | Organizational learning; increased safety | Organizations focused on continuous improvement | Encourages honest reporting; identifies systemic issues |
| Implement Tiered Escalation Procedures | Medium – defining tiers and triggers | Moderate – staffing multiple levels | Timely expert involvement; accountability | Environments with varied incident severities | Efficient resource use; predictable response flow |
| Develop Effective Communication Protocols | Medium – templates and roles definition | Moderate – communication tools and training | Transparent updates; managed expectations | Incidents impacting multiple audiences and stakeholders | Reduces rumors; maintains trust |
| Automate Incident Detection and Response | High – tool setup and ongoing tuning | High – integration and maintenance | Faster detection and initial response | High-volume, routine incidents requiring 24/7 monitoring | Dramatically reduces detection time; frees human resources |
Take Control of Your Incident Response with Resolution Reichert
Mastering incident management best practices is crucial for any organization striving for operational efficiency and resilience. Throughout this article, we’ve explored key strategies, from establishing a clear incident classification framework and implementing comprehensive response plans, to maintaining a single source of truth and conducting blameless post-mortems. By prioritizing tiered escalation procedures, effective communication protocols, and even automating incident detection and response, you can significantly reduce downtime, minimize business impact, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. Remember, the most important takeaways are proactive planning and a commitment to learning from every incident. These combined efforts transform reactive firefighting into proactive problem-solving, creating a more stable and reliable environment for your teams and customers.
Implementing these incident management best practices empowers your organization to navigate disruptions effectively, minimizing their impact on productivity, customer satisfaction, and ultimately, your bottom line. Taking control of your incident response transforms potential chaos into manageable situations, allowing your teams to focus on delivering value rather than constantly putting out fires.
Want to further enhance your incident management capabilities and ensure seamless workflows even during planned absences? Explore Resolution Reichert Network Solutions GmbH’s Out of Office Assistant for Jira Cloud. This tool automates handovers and maintains uninterrupted progress, reducing response times and minimizing disruptions, contributing directly to your overall incident management strategy. Learn more and optimize your incident response today by visiting Resolution Reichert Network Solutions GmbH.
