Let’s break down what “provisioning” really means. At its heart, provisioning is simply about preparing and allocating a resource to make it ready for use.
Think about what happens when a new employee joins your team. You don’t just point them to an empty desk. You get their workstation set up, their computer configured, all their necessary accounts activated, and access granted to the software they’ll need. That whole “getting ready” process? That’s provisioning.
What Is Provisioning in Simple Terms?

While the term might sound a bit technical, the idea is something we encounter all the time. Provisioning is the crucial step that takes a resource from just existing to being fully operational and ready for its job.
For instance, when that new team member needs to jump into a project, they need access to tools like Jira and Confluence right away. The act of creating their accounts and assigning the correct permissions is what we call user provisioning. It’s what lets them be productive from day one instead of waiting around for access.
Similarly, if a developer needs a new server to build an application, the process of assigning the right amount of computing power, memory, and storage is known as server provisioning. The core idea is the same: preparation and allocation.
Provisioning Across Different Fields at a Glance
While our focus is on IT and user management, it’s helpful to see how this fundamental concept of “preparation” applies in other areas. This quick table shows how the term ‘provisioning’ is used across various professional contexts.
| Context | What It Means | Core Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| IT (User Management) | Creating user accounts, assigning permissions, and granting access to software. | To enable employees to access the tools they need for their jobs securely. |
| Telecommunications | Activating a new phone line or setting up mobile services for a customer. | To make a communication service available and functional for a subscriber. |
| Cloud Computing | Allocating virtual servers, storage, and other cloud infrastructure on demand. | To provide scalable and flexible computing resources for applications and services. |
| Finance & Accounting | Setting aside funds for a known future liability or expected expense. | To ensure financial preparedness and accurate reporting of a company’s financial health. |
As you can see, whether you’re talking about a user, a server, or a budget line item, provisioning is all about getting things ready for a specific purpose.
The Role of Automation
Now, imagine manually setting up every single resource for every single user. It would be incredibly time-consuming and, frankly, a recipe for human error. One wrong permission setting could lead to a data breach or simply a frustrated employee who can’t do their job. This is where automation changes everything.
Automated systems can handle these repetitive setup tasks based on rules you define. This ensures every user gets the right access, every time, without an admin having to click through dozens of screens.
A fantastic example of this in action is Just-In-Time (JIT) provisioning. With JIT, a user’s account is created automatically the very first time they try to log into an application. It’s an on-the-fly process that dramatically cuts down on administrative work and boosts security by ensuring accounts only exist when they’re actually needed.
This automated approach doesn’t just make onboarding faster; it makes ongoing management a whole lot simpler. To see how this works in more detail, you can dive into the specifics of Just-In-Time provisioning. By understanding how provisioning works in different contexts, you can really start to see why it’s so critical for building an efficient, secure, and smoothly-run organization.
How IT Provisioning Powers Modern Business
In the world of IT, provisioning is where the magic happens. It’s the foundational process of setting up all the necessary IT infrastructure for your organization and then giving people the keys—granting them access to the resources they need to do their jobs. This covers everything from servers and cloud services to the specific applications your teams rely on every single day.
It’s easy to mix up provisioning with configuration, but they are two distinct steps. Think of it like building a house:
- Provisioning is the ‘what’. It’s about laying the foundation and framing the walls. In IT terms, this means allocating a virtual server with a specific amount of CPU, memory, and storage. You get the raw materials ready.
- Configuration is the ‘how’. This is furnishing the house. It’s the step that follows provisioning, where you install the operating system, set up security rules, and load the software onto that server you just provisioned.
You can’t furnish a room that doesn’t exist. Provisioning always comes first.
The Shift From Manual To Automated
Not too long ago, provisioning was a painful, manual slog. An IT admin would get a ticket, walk over to a server rack, physically set it up, install software from a disc, and then manually punch in user account details. This whole ordeal could take days, if not weeks, putting a major brake on new projects and company growth.
Thankfully, things have changed. Today, in the tech world, provisioning is all about automation. Large companies now rely on automated provisioning to spin up resources in cloud and hybrid environments, slashing setup times from days down to a few minutes. This speed is a game-changer for staying agile and saving a ton of money. If you want a deep dive on this, IBM offers a great explanation of provisioning and its impact.
But this move to automation is about more than just going faster; it’s about building a stronger, more secure business.
By automating these foundational steps, companies eliminate the risk of human error, ensure consistency across all environments, and free up skilled IT professionals to focus on strategic initiatives instead of repetitive setup tasks.
This efficiency has become a non-negotiable part of modern business. The ability to deploy resources on the fly means companies can scale up or down as needed, react to market shifts instantly, and get their teams working without any bottlenecks. If you’re curious about how this applies to service delivery, you should check out our guide on IT service management automation.
Ultimately, great IT provisioning is the invisible engine that helps a company move faster, grow smarter, and operate more securely.
Managing the Employee Lifecycle with User Provisioning
Forget servers and hardware for a moment. One of the most critical, day-to-day IT processes for any company is user provisioning. Think of it as the complete journey of an employee’s digital identity—from creating their accounts on day one, to managing their access levels, and finally, securely shutting everything down when they leave.
When a new person joins the team, user provisioning is what gets them in the door, digitally speaking. It’s the process that grants them access to their email, collaboration tools like Slack or Teams, and of course, project management platforms like Atlassian Jira. Getting this right from the start is especially important for distributed teams. A solid practical guide to onboarding remote workers will always emphasize getting system access sorted immediately, so new hires can hit the ground running.
The basic flow is pretty straightforward, but the details matter.
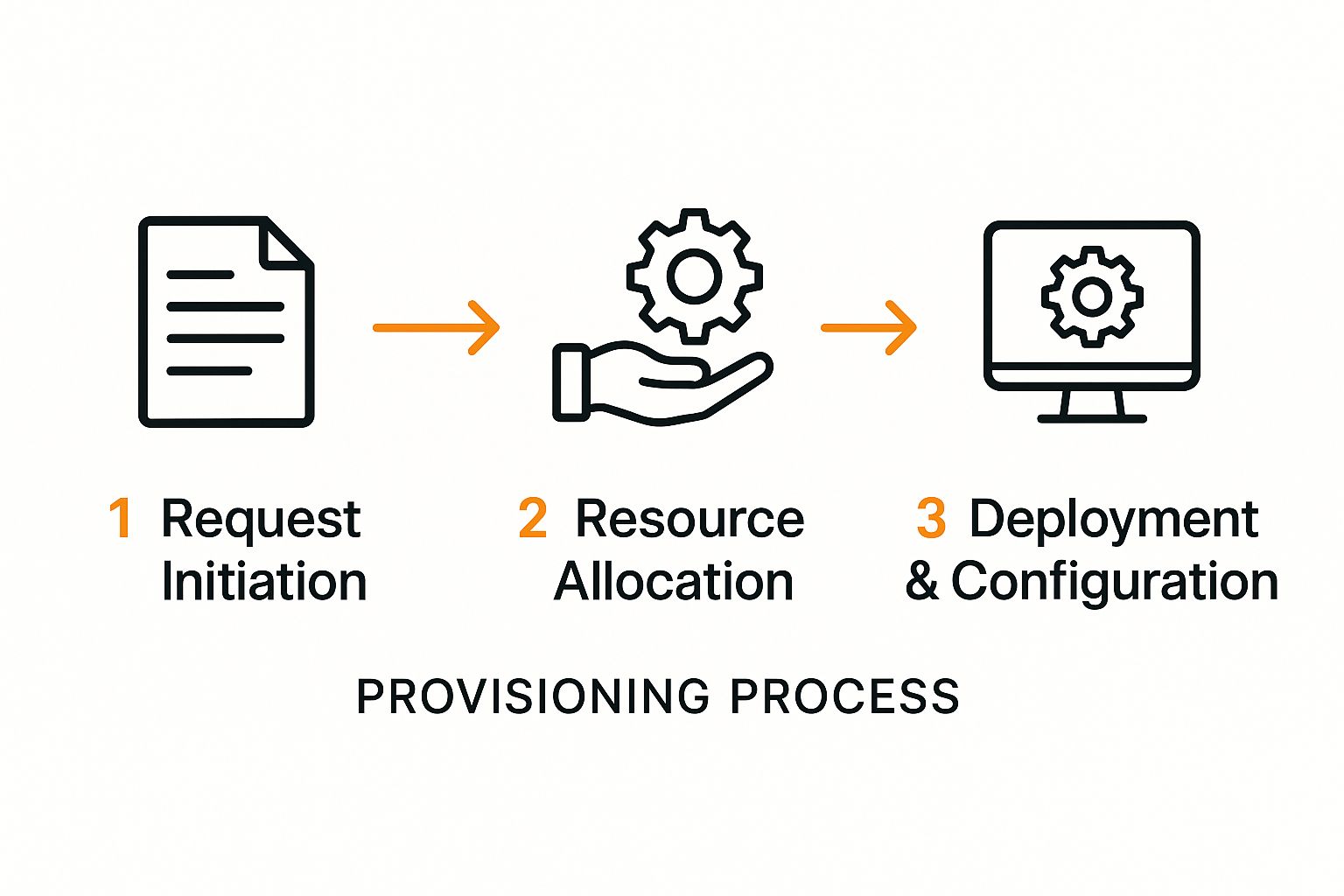
As you can see, it all starts with a request, moves to allocating the right resources (like software licenses), and ends with deploying and configuring everything for that specific user.
The Importance of Proper Deprovisioning
Now, what happens when an employee leaves? This is where things get serious. Granting access is one thing; revoking it is another. User deprovisioning—the formal process of removing a user’s access to all company systems—is a massive security checkpoint.
If a former employee’s account remains active, they become a lurking threat. They could potentially walk away with sensitive company data or intellectual property long after their final day.
Ineffective deprovisioning isn’t just a hypothetical risk. It’s a gaping security hole that leads directly to data breaches and painful compliance failures. You absolutely must have a rock-solid process for cutting off all access the moment an employee departs.
Take Atlassian tools, for example. An admin for a Jira instance needs to be incredibly diligent about who can access which projects and what they can do there.

In a platform like Jira, provisioning isn’t just about creating an account. It’s about assigning that user to specific roles with very granular permissions, making sure they only see and interact with what’s relevant to their job. This not only tightens security but also helps with software license management by making sure you aren’t paying for accounts that are no longer needed. For a deeper dive, check out our complete guide to user provisioning and deprovisioning.
Fueling Decisions with Data Provisioning

So far, we’ve covered the nuts and bolts of setting up infrastructure and user accounts. But what about the information that flows through those systems? That’s where data provisioning comes in. Think of it as the critical process of getting the right data from all its different sources, cleaning it up, and delivering it to the people and tools that need it for analysis.
Let’s use a real-world example. Imagine a financial services firm trying to catch credit card fraud. Their fraud detection system is only as good as the data it receives. It needs a constant, real-time feed of transaction information to work its magic. Data provisioning is the engine that makes this happen, pushing the correct information to the system at the exact moment it’s needed to flag a bogus purchase.
Why Data Access Is a Competitive Edge
In a world drowning in information, just having data is no longer enough. The real power lies in having the right data, properly organized and delivered where it can do the most good. This is where data provisioning truly shines, turning a jumble of raw information into fuel for smarter choices. It’s the foundation for making sound, data-driven decisions that can steer a company toward real growth.
A huge piece of this puzzle is blending information from different systems. If you want to go deeper on this specific topic, there are some great resources out there on marketing data integration that really break it down.
Data provisioning is like the central nervous system for business intelligence. It connects the brain (your analysts and decision-makers) with the sensory inputs (raw data from sales, ops, and customers), allowing the entire organization to react quickly and intelligently.
This ability is absolutely vital in today’s complex cloud environments. In fact, it’s so important that enterprises now dedicate up to 40% of their data management budgets just to provisioning and related integration work. This massive investment shows just how crucial it is for staying competitive. You can discover more insights about data provisioning on accelario.com.
Understanding a Provision in Accounting
While IT teams are busy getting resources ready for users, accountants use the word provisioning for something completely different. In the financial world, it’s all about setting aside funds to cover a future expense that is likely to happen, but isn’t certain just yet. This isn’t just about putting cash in a shoebox. A provision is a formal liability recorded on a company’s balance sheet, and it directly impacts reported profits.
Think of it like financial forecasting for costs you know are coming down the pipeline. A classic example is a company creating a provision for bad debts because they know, based on experience, that a certain percentage of customers simply won’t pay their bills. This simple act paints a much more honest picture of the company’s real financial health.
How Financial Provisions Work
Provisions are a cornerstone of responsible corporate governance. By recognizing potential future costs today, companies avoid nasty financial surprises down the road and give investors a more transparent look at their books.
Here are a few common places you’ll see provisions in action:
- Warranty Claims: A manufacturer estimates how much they’ll spend on future repairs for products they’ve already sold and sets aside the funds to cover it.
- Bad Debts: Companies look at their payment history to estimate uncollectible invoices. Provisions here often fall between 1% to 5% of their outstanding credit. To learn more about how businesses handle this, check out this guide on provisions in accounting on happay.com.
- Restructuring Costs: When a company plans for future layoffs or office closures, it allocates funds ahead of time through a provision.
A provision is a formal acknowledgment of a likely future obligation. It’s the difference between hoping for the best and preparing for the probable, creating a buffer that enhances financial stability.
Oddly enough, this financial practice shares a similar spirit with how IT teams plan for user lifecycle events. Both are about proactively managing resources—whether financial or digital—to ensure things run smoothly. Our deep dive into provisioning Confluence users at Hansgrohe shows just how much proactive planning can save you in the long run.
Frequently Asked Questions About Provisioning

We’ve covered a lot of ground on provisioning, from setting up IT resources to managing user accounts. As with any deep topic, a few questions tend to pop up again and again. Let’s tackle them head-on to clear up any lingering confusion.
Think of this as a quick-reference guide. Getting these concepts straight is key, because the word “provisioning” means very different things depending on whether you’re talking to an IT admin or an accountant. Nailing these distinctions is vital for efficiency, security, and solid financial reporting.
What Is the Difference Between Provisioning and Configuration?
This is easily the most common point of confusion, and the best way to understand it is to think about the order of events. It’s really a two-step dance.
Provisioning is the ‘what’. It’s all about creating or allocating the resource in the first place. When a new virtual server is requested, provisioning is the act of carving out a specific amount of CPU, RAM, and storage for it.
Configuration is the ‘how’. This is what happens after the resource exists. It’s the process of setting that resource up to do its job—installing the operating system, applying security policies, or loading the specific applications it needs to run.
Simply put: provisioning gives you an empty room; configuration is how you furnish it.
Is an Accounting Provision the Same as Savings?
Not at all. While both involve putting money aside, they serve fundamentally different purposes in finance and have very different impacts on the books.
Savings are just funds a company holds for general use. They don’t touch the reported profits on an income statement. An accounting provision, however, is a formal recognition of a probable future liability.
It’s an expense recorded on the balance sheet that directly reduces the company’s current profits. This gives a much more accurate picture of the company’s true financial health by accounting for costs that are expected but haven’t been paid yet.
For example, a company might create a provision for future warranty claims. This isn’t just stashing cash away; it’s a formal acknowledgment of a real, expected cost.
Why Is User Deprovisioning So Important?
User deprovisioning—the process of revoking a user’s access when they leave the company—is absolutely critical for modern cybersecurity. When someone leaves, failing to immediately and completely shut down their access opens up a massive security hole.
This isn’t just a theoretical risk. A forgotten active account is a prime target. It could be used by a disgruntled ex-employee or an external attacker to waltz right in and access sensitive company data, customer details, or valuable intellectual property.
Proper deprovisioning is not just good IT hygiene; it is an essential security control. It’s a non-negotiable step to protect your organization from data breaches, compliance fines, and serious financial loss.
Are you tired of manually tracking user activity and paying for Atlassian licenses that go unused? resolution Reichert Network Solutions offers User Deactivator, the automated solution to keep your user directory clean and your costs down. Automatically disable inactive users, manage permissions in bulk, and ensure your organization is secure and compliant. Learn how you can optimize your license spending today by exploring User Deactivator.