Think of language localization as the art of making your product or content feel like it was born and raised in a new market. It’s much deeper than just swapping words from one language to another. It’s about adapting the entire experience to feel completely natural and intuitive for a local audience.
Going Beyond Translation with Language Localization

It’s easy to get translation, localization, and another term—internationalization—mixed up. They all deal with taking a product global, but they play very different roles in the process.
- Translation is the foundation. It’s about accurately converting text from a source language to a target language.
- Internationalization (i18n) is the technical prep work. It means designing your software or product from the ground up so that it can be adapted for different languages and regions without needing to be re-engineered.
- Localization (L10n) is the final, crucial adaptation layer. It takes the translated text and the internationalized product and fine-tunes everything for a specific market.
Here’s a quick breakdown to make the distinction crystal clear:
Comparing Translation, Localization, and Internationalization
| Concept | Primary Goal | Scope of Work | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Translation | Convert text accurately | Translating words and sentences from one language to another. | Changing “Add to Cart” in English to “Ajouter au Panier” in French. |
| Localization | Create a native experience | Adapting all content (text, images, formats, currency) to cultural and functional norms. | Changing the date format from MM/DD/YYYY to DD/MM/YYYY, updating currency from USD to EUR, and replacing a photo of a mailbox with a culturally relevant one. |
| Internationalization | Enable future adaptation | Designing and coding the product to handle different languages and regional standards easily. | Building a website’s backend so it can display dates, currencies, and text in multiple formats without breaking. |
As you can see, they build on each other. You can’t have good localization without solid translation, and both are much easier with a well-internationalized product.
The Real Goal: Earning Trust Through Adaptation
So why go through all this trouble? It comes down to one word: trust. When a customer interacts with a product that not only speaks their language but also understands their local customs, it feels familiar and reliable. You’re breaking down barriers and showing that you genuinely care about their experience.
This isn’t just about warm feelings; it’s smart business. Imagine an e-commerce site perfectly translated into German but only offering credit card payments. You’d lose a huge chunk of sales because many German shoppers prefer options like direct bank transfers or PayPal. That’s a classic localization miss.
True localization is what transforms your product from being merely usable in a foreign market to being genuinely preferred. It’s the difference between a visitor and a loyal customer.
The demand for this level of detail is exploding. The global language services market, which includes localization, was valued at $60.68 billion in 2022 and is expected to hit $96.21 billion by 2032. This isn’t just a niche service anymore; it’s a fundamental part of any serious global growth strategy. For a deeper dive, you can explore the full language services market research.
Ultimately, investing in localization isn’t just a cost of doing business abroad. It’s an investment in building a sustainable, successful international brand.
So, Does Localization Actually Grow Your Business?
Let’s move past the theory. How does making your content feel truly local actually translate into real-world results? It’s simple: language localization isn’t just another expense on a spreadsheet. It’s one of the most powerful engines for breaking into new markets and becoming a dominant player.
Think about global giants like Netflix or Spotify. Their success didn’t just come from slapping on some subtitles. They went all-in, localizing the entire user experience. They curated playlists that vibed with local music tastes, promoted regional artists, and made sure you could pay with whatever method was common in that country. This deep level of adaptation creates a product that doesn’t just feel translated—it feels like it was made for them.
Boost Conversions and Build a Loyal Following
When customers feel like you “get” them, they’re far more likely to click that “buy” button. Adapting your product, marketing, and support to the little details of a local culture removes friction and builds a massive amount of trust. The direct result? Higher conversion rates. But it’s not about a one-time sale; you’re laying the groundwork for real, lasting customer loyalty.
This powerful connection is exactly why the localization industry is booming. The market was pegged to hit $71.7 billion in 2024 and is on track to jump to $75.7 billion in 2025. This isn’t just random growth; it’s fueled by smart companies realizing that localization is no longer optional if you want to compete. You can dive deeper into these localization industry growth trends to see for yourself.
A perfectly adapted user experience transforms a one-time buyer into a loyal advocate for your brand. Localization is the mechanism that builds this bridge of trust, turning cultural understanding into a significant competitive edge.
And this connection doesn’t end after the purchase. Providing customer support in someone’s native language is absolutely critical for keeping them around. When users can get help without struggling through a language barrier, it radically improves their satisfaction and cements their good feelings about your brand. We’ve seen this time and time again in these five use cases for a multilingual service desk.
Supercharge Your Global SEO Strategy
Localization is also a secret weapon for your global search engine optimization (SEO) strategy. Just translating keywords from one language to another is a recipe for failure. Real global SEO means getting inside the heads of local searchers and targeting the specific slang, regional terms, and search habits that a machine would totally miss.
- Target Local Keywords: Someone in London might search for “holiday deals,” but a person in New York is looking for “vacation packages.” Localization makes sure you’re showing up for the right terms in every single market.
- Improve Local Rankings: Search engines are all about relevance. A fully localized website—complete with the right currency, date formats, and local contact info—screams relevance to Google for that specific region.
- Enhance User Engagement: When you give people a seamless, culturally familiar experience, they stick around longer. Your bounce rates drop. These positive signals are like gold to search engine algorithms, giving your rankings a serious boost.
At the end of the day, language localization ensures your brand isn’t just visible in new markets. It makes you prominent and easy to find for the exact customers you’re trying to reach.
Your Step-By-Step Language Localization Workflow
A solid language localization project doesn’t just happen. It’s the result of a carefully structured workflow that guides everything from the initial idea to the final product launch, making sure nothing gets lost in translation. If you try to cut corners, you’re just setting yourself up for expensive fixes and a confusing experience for your new audience.
Think of it like building a house. You wouldn’t dream of painting the walls before the foundation is poured and the framing is complete. Localization works the same way. You need to get the technical foundation right before a single word gets translated or a single image gets swapped out. Following a methodical process ensures every piece fits together perfectly.
This chart lays out the core stages of a typical language localization process.
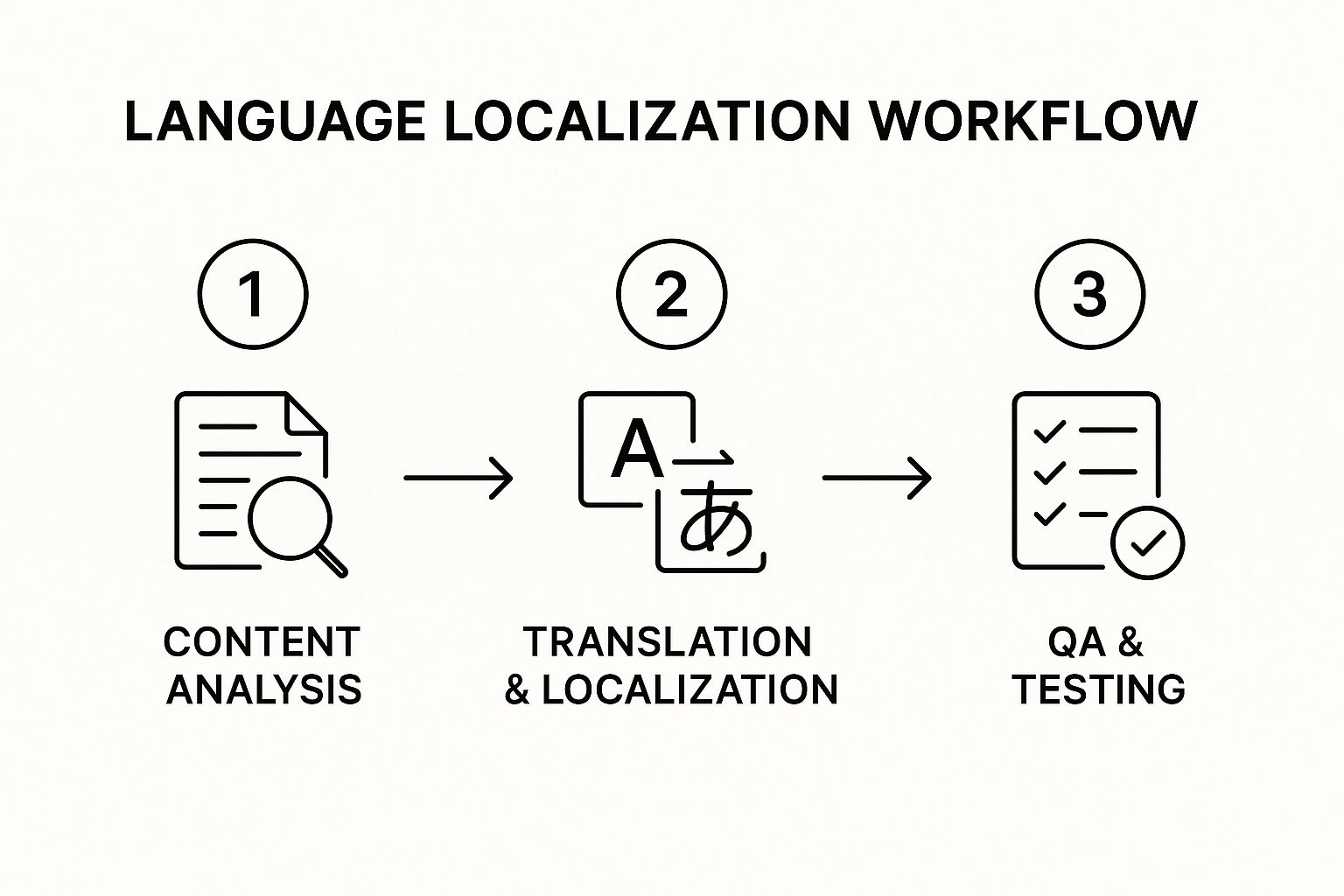
As you can see, it’s a logical flow from preparation to execution and finally to verification. This progression is key to preventing small issues from turning into major headaches down the road.
Phase 1: Internationalization and Content Preparation
The first real step isn’t about translation at all—it’s about internationalization (i18n). This is the technical prep work done by developers. They go into the product’s code and separate all the text from the programming logic. This critical step ensures the software can handle different languages, character sets, and regional formats (like dates, times, and currencies) without crashing or displaying gibberish.
With the technical side ready, the focus shifts to preparing the content itself. A localization manager takes the lead here, typically by:
- Scoping the project: They identify every piece of content that needs localizing. This isn’t just the obvious UI text; it includes error messages, help articles, marketing emails, and more.
- Creating a localization kit: This is the project’s bible. It contains style guides, glossaries of key terminology, and any existing translation memory files to keep the brand’s voice consistent.
- Assembling the right team: They bring together a team of professional linguists, editors, and cultural experts who are native speakers of the target language.
This initial prep phase is hands-down the most important part of the entire workflow. Nailing the internationalization and providing crystal-clear instructions will prevent the vast majority of common localization mistakes, saving you an enormous amount of time and money later on.
Phase 2: Translation and Cultural Adaptation
Now that the groundwork is laid, the real translation can kick off. This is where linguists take the source text and convert it into the target language. But a truly great localization process is about much more than just swapping words.
This is the “localization” (L10n) part, where deep cultural adaptation makes all the difference. It means adjusting elements beyond just the text:
- Imagery and Colors: Replacing photos or graphics that might be confusing, irrelevant, or even offensive in the new market.
- Layout and Design: Tweaking the user interface to handle text that expands or shrinks. German words, for instance, are often much longer than their English counterparts and can easily break a fixed layout.
- Local Norms: Modifying examples, currencies, payment methods, and units of measurement to feel familiar and intuitive to local users.
Phase 3: Quality Assurance and Deployment
Once everything is adapted, the project moves into the quality assurance (QA) stage. And no, this isn’t just running a quick spell-check. A completely separate team of linguists needs to review the localized content in context—meaning they use the actual software, app, or website. They’re hunting for linguistic mistakes, cultural missteps, and any functional bugs that the localization process might have introduced.
After the QA team gives their final sign-off, the localized version is ready to go live. But the job isn’t quite done. The last step is to gather feedback from actual users to guide future updates and improvements. Monitoring this data is invaluable, and you can even explore how to build an automatic translation report for your business to track performance and ROI with real numbers.
Using Technology to Scale Your Localization Efforts
Let’s be honest: trying to manage language localization across multiple markets by hand is a recipe for disaster. It’s not just hard; it’s nearly impossible to do well. If you want to succeed on a global scale, you need a solid technology stack to automate your work, keep everything consistent, and hit your deadlines without letting quality slip. This is where the right tools become the backbone of your entire strategy.
Today’s best localization efforts are powered by a suite of connected technologies. These systems talk to each other to create a smooth flow of content—from the moment it’s written to its final translated deployment. The whole process becomes faster, cheaper, and a lot less painful.
The Core Technology Powering Localization
Two pieces of this puzzle are absolutely fundamental: the Translation Management System (TMS) and Translation Memory (TM).
- Translation Management System (TMS): Think of a TMS as the central command center for all your localization projects. It’s the software that automates the entire workflow. It handles files, doles out tasks to linguists, and lets you track everything from start to finish. To really scale up, understanding the different workflow automation benefits is key to getting the most out of your TMS.
- Translation Memory (TM): This is a database that cleverly stores every sentence, phrase, and bit of text you’ve ever had translated. The next time a linguist starts a project, the TM automatically suggests translations for any text it recognizes. This makes the work dramatically faster and keeps your brand voice consistent.
When a TMS and a TM work together, you never pay to translate the same sentence twice. This partnership is what slashes costs and ensures your brand sounds like your brand, no matter where in the world your content is read.
AI and the Human-in-the-Loop Model
Artificial intelligence, particularly Neural Machine Translation (NMT), has added a powerful new layer to this toolkit. But this isn’t about robots taking over. The smartest approach is a “human-in-the-loop” model. NMT provides a surprisingly good first draft, which a professional human translator then polishes to perfection.
This combination of machine speed and human touch is what’s fueling massive growth in the industry. Thanks to AI, the language services market is expected to jump from USD 78.12 billion in 2024 to a staggering USD 131.75 billion by 2033. This boom is happening because technology is making large-scale localization more accessible and faster than ever before.
Integrating Localization Into Your Daily Workflows
The real magic happens when this technology is plugged directly into the tools your teams use every single day. For instance, customer support teams on Jira Service Management can get a huge boost from apps that embed translation right into their ticketing system.
This is what it looks like when an app like Issue Translation for Jira Service Management is built right into the interface.

By putting the translation controls directly in the Jira issue view, agents don’t have to jump between different windows or platforms. It removes all the friction and makes multilingual support a completely natural part of their job. If you want to dig deeper into this, our article on using Google Translate for Jira and JSM has more details.
When you bring translation capabilities into your existing platforms, you break down silos. You empower every team—from marketing to support—to communicate globally without having to become localization experts themselves.
Essential Best Practices for Effective Localization

Jumping into language localization without a plan is a recipe for disaster. It’s a sure-fire way to blow your budget, miss deadlines, and, worst of all, damage your brand’s reputation in a market you’re trying to win over. To get a real return on your investment, you need a structured, proactive approach.
Think of these best practices as the guardrails on your highway to global expansion. They keep your project from veering off course, ensuring every piece of content is consistent, high-quality, and culturally on-point.
The first move, and arguably the most important, is to get strategic about which markets you target. Don’t just throw darts at a map. Dig into your data—look at website traffic, market size, and what your competitors are doing. A whopping 76% of online shoppers prefer buying from sites that provide information in their own language. Data-driven decisions ensure you put your money where it counts.
Establish a Solid Foundation
Once you’ve picked your target markets, you need to build a framework that can scale. This all starts with creating clear, detailed resources for your translation and localization teams. These aren’t nice-to-haves; they are absolutely essential for keeping your brand identity intact across different languages.
Your core assets should always include:
- A Comprehensive Style Guide: This is your brand’s personality on paper. It dictates the tone of voice, grammar rules, and formatting, making sure your brand feels like your brand, whether it’s in English or Japanese.
- A Detailed Glossary: Also known as a termbase, this is a master list of your key industry jargon and company-specific terms with their pre-approved translations. It’s your secret weapon against inconsistency.
A well-defined style guide and glossary are the single most effective tools for preventing brand dilution during localization. They are the source of truth that aligns every linguist with your company’s voice and standards.
Focus on Quality and Context
While technology is great for speed, quality assurance is still a deeply human game. For high-stakes content like a major marketing campaign or your app’s user interface, you absolutely need professional human translators. They bring a level of cultural understanding and creative flair that machine translation simply can’t match. You can dive deeper into this balancing act by reading these insights on automatic translations.
On top of that, you can’t review translations in a vacuum. A critical best practice is in-context review, where linguists check the translated text inside the actual app, website, or software. This is where you catch the kind of problems that are completely invisible on a spreadsheet, such as:
- Text that overflows its container (a classic issue when translating into verbose languages like German).
- Buttons or links with clunky or nonsensical translations.
- Contextual mistakes where a phrase is technically correct but makes no sense with the surrounding graphics or text.
By weaving these practices into your localization workflow from the very beginning, you build a repeatable, scalable process for global success. It’s how you minimize headaches and maximize your impact.
Common Questions About Language Localization
Jumping into language localization usually sparks a lot of practical questions about costs, tools, and the right way to approach it. Getting clear, real-world answers is the best way to move forward with confidence and sidestep some expensive mistakes.
Let’s tackle some of the most common questions we hear from businesses planning to take their products and services global.
How Much Does Language Localization Cost?
There’s really no single price tag for language localization. The final cost swings pretty wildly based on a few key things. The languages you’re targeting are a big one; common pairings like English to Spanish will almost always be cheaper than translating into a less common language like Icelandic.
A few other major factors drive the cost:
- Content Volume: This is the total number of words you need to get localized. Simple enough.
- Technical Complexity: There’s a world of difference between localizing a simple webpage and adapting a complex software application with lots of moving parts.
- Quality Assurance (QA): How much review and testing do you need? A more rigorous QA process will naturally affect the final price.
You’ll also see different pricing models. Per-word rates are the most common by far, but some projects might be priced by the hour or as a flat project fee. The most important thing is to stop thinking of localization as a cost and start seeing it as a strategic investment. When you get it right, localization opens up entirely new revenue streams and builds incredible customer loyalty, delivering a return that speaks for itself.
Can I Just Use AI or Machine Translation?
Machine translation (MT) has gotten shockingly good, but it’s a powerful tool, not a silver-bullet solution. Just running your customer-facing content, marketing copy, or anything that needs to capture your brand’s voice through raw MT is a huge gamble. It can easily spit out awkward phrases, damage your brand’s reputation, and create a genuinely bad user experience.
The smartest approach is what we call a “human-in-the-loop” model. Here, machine translation does the heavy lifting and provides a solid first draft. Then, a professional human linguist reviews, edits, and culturally polishes it. This process is known as Post-Editing Machine Translation (PEMT).
This hybrid method gives you the raw speed of AI combined with the nuance, cultural awareness, and quality control that only a human expert can provide. As the technology keeps getting better, the line between machine and human output is getting blurrier and blurrier, something you can dig into deeper in this analysis of whether Google Translate can pass the Turing test. This balanced strategy gives you a scalable, high-quality solution that fits the demands of modern business.
How Do I Choose the Right Languages to Localize For?
Picking your target languages should be driven by data, not a gut feeling. A phased approach is almost always the best way to go. Kick things off by digging into your current website traffic and user data. Where is your international audience already coming from? That’s your first clue.
Next, it’s time for some market research. Look for regions that have:
- High demand for the kind of product or service you offer.
- A favorable competitive landscape where you can actually make some noise.
- A strong Total Addressable Market (TAM) with real purchasing power.
And don’t forget to consider languages with a massive online footprint, like Spanish, Mandarin, and Arabic. The most effective strategy is to pick one to three high-priority languages, get them launched, and carefully measure the ROI. Use those results to build your business case and guide your expansion into the next set of markets.
Ready to break down language barriers in your customer support? resolution Reichert Network Solutions GmbH offers Issue Translation for JSM, the top-rated app that embeds seamless, AI-powered translation directly into Jira Service Management. Empower your agents to deliver world-class support in any language. Try Issue Translation for JSM for free today.
